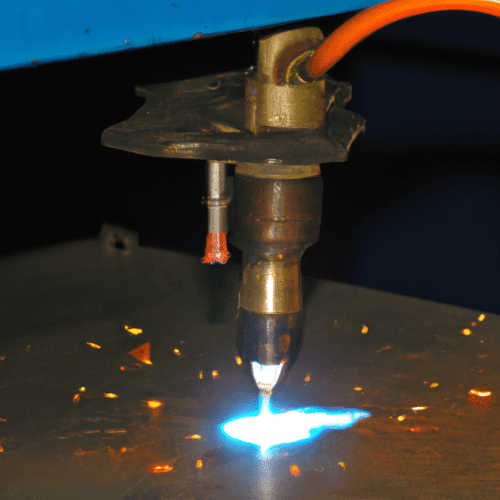
A plasma torch is a device that uses an electric arc to generate a stream of hot ionized gas, or plasma. It is used in a variety of industrial applications, such as welding, cutting, and surface treatment. The plasma torch consists of a power supply, a gas supply, and a torch head. The power supply provides the electrical energy to create the arc, while the gas supply provides the fuel for the arc. The torch head contains the electrodes and nozzle, which direct the arc and the gas flow.
When the power supply is activated, an electric arc is created between the electrodes in the torch head. This arc is very hot, and it ionizes the gas that is flowing through the torch head. This ionized gas, or plasma, is then directed out of the nozzle at a high velocity. The plasma is hot enough to melt or cut through metal, depending on the application.
The plasma torch is a versatile tool that can be used for a variety of applications. It is used in welding, cutting, and surface treatment. In welding, the plasma torch is used to join two pieces of metal together. The plasma melts the metal, and the molten metal is then allowed to cool and form a strong bond. In cutting, the plasma torch is used to cut through metal. The plasma melts the metal, and the molten metal is then blown away by the high velocity of the plasma stream. In surface treatment, the plasma torch is used to clean or etch the surface of a metal. The plasma melts the surface of the metal, and the molten metal is then blown away by the high velocity of the plasma stream.
The plasma torch is a powerful and versatile tool that can be used in a variety of industrial applications. It is important to use the plasma torch safely and correctly, as it can be dangerous if not used properly.
How does a plasma cutting torch work?
A plasma cutting torch is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using an electrical arc to heat and melt the material, while a high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) is used to blow away the molten material. The plasma cutting torch consists of a power supply, a torch handle, and a consumable electrode and nozzle.
The power supply is the main component of the plasma cutting torch. It is responsible for providing the electrical current to the torch. The power supply is typically connected to a wall outlet or a generator. It is also responsible for controlling the amperage and voltage of the electrical current.
The torch handle is the part of the plasma cutting torch that the operator holds. It contains the electrode and nozzle, which are the parts that actually cut the material. The electrode is a consumable part that is made of copper and is responsible for creating the electrical arc.
How are plasma torches powered?
Plasma torches are powered by a combination of electricity and gas. The electricity is used to create an electrical arc between two electrodes, which is then used to heat a gas, such as argon, to a very high temperature. This creates a plasma, which is a hot, ionized gas that is used to cut, weld, or heat materials. The gas is usually supplied from a pressurized tank, and the electricity is supplied from a power source, such as a generator or a wall outlet. The combination of electricity and gas creates a powerful arc that is capable of cutting through metal and other materials.
Does a plasma torch need gas?
Yes, a plasma torch does need gas in order to operate. Plasma torches use a combination of gases, typically a mixture of argon and hydrogen, to create an electric arc that is used to cut and weld metal. The gas is fed into the torch through a nozzle, where it is ionized by an electric current. This creates a plasma arc that is hot enough to cut through metal. The gas also helps to protect the metal from oxidation and other damage caused by the heat of the arc. The gas also helps to stabilize the arc and provide a consistent cutting or welding temperature. The type and amount of gas used will depend on the type of material being cut or welded, as well as the thickness of the material.
How does a plasma cutter operate?
A plasma cutter is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using an electrical arc to heat and melt the material, which is then blown away by a high-velocity stream of gas, usually compressed air. The arc is created by an electrical current that passes between an electrode and the material being cut. The electrode is connected to a power supply, which provides the electrical current. The power supply is usually a transformer that steps down the voltage from the power line to a level that is safe for the operator.
The plasma cutter works by creating an electrical arc between the electrode and the material being cut. The arc is created when the electrical current passes through the air between the electrode and the material. The air is heated to a temperature of around 20,000 degrees Celsius, which is hot enough to melt the material. The molten material is then blown away by the high-velocity stream of gas, usually compressed air.
What is a disadvantage of plasma cutting?
A disadvantage of plasma cutting is that it can be difficult to control the cut quality. Plasma cutting is a thermal cutting process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials. The plasma arc is created by an electrical arc between an electrode and the workpiece. The plasma arc is then directed through a constricting orifice, which increases the velocity of the plasma stream and focuses it onto the workpiece. The high velocity of the plasma stream and the heat generated by the arc cause the material to melt and be blown away from the cut.
The quality of the cut is determined by the speed and accuracy of the plasma arc, the type of gas used, the size of the orifice, and the type of material being cut. The speed and accuracy of the plasma arc can be difficult to control, which can lead to poor cut quality. Additionally, the heat generated by the plasma arc can cause the material to warp or distort, which can also lead to poor cut quality.
Is a plasma cutter better than a torch?
A plasma cutter is a tool that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It is often used in industrial applications such as welding, fabrication, and metalworking. A torch, on the other hand, is a tool that uses a flame to cut through materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
When it comes to deciding which tool is better, it really depends on the job at hand. A plasma cutter is generally more efficient and precise than a torch, and it can cut through thicker materials with greater accuracy. It is also much faster than a torch, and it can be used to cut intricate shapes and patterns. However, a plasma cutter is more expensive than a torch, and it requires a power source to operate.
On the other hand, a torch is much cheaper than a plasma cutter, and it does not require a power source. It is also much easier to use than a plasma cutter, and it can be used to cut through thinner materials with greater accuracy.
What kind of gas do you use for a plasma cutter?
A plasma cutter is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using an electrical arc to heat and melt the material, which is then blown away by a high-velocity stream of gas. The gas used in a plasma cutter is typically a combination of compressed air and inert gases such as argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen. The type of gas used will depend on the type of material being cut and the thickness of the material. For example, argon is typically used for cutting thin materials such as sheet metal, while nitrogen is used for thicker materials such as steel plate. The gas mixture is usually adjusted to provide the optimal cutting performance for the material being cut.
How many volts does a plasma cutter produce?
A plasma cutter typically produces between 15 and 40 volts of direct current (DC). The exact voltage depends on the type of plasma cutter being used, as well as the type of material being cut. For example, a plasma cutter used to cut thin sheet metal may require a lower voltage than one used to cut thicker materials. Additionally, some plasma cutters are designed to operate at a higher voltage than others. Generally, the higher the voltage, the faster the cutting speed and the better the cut quality. It is important to note that the voltage of a plasma cutter should never exceed the manufacturer’s recommended maximum voltage. Doing so can cause damage to the machine and may even be dangerous.
Do all plasma cutters need air compressor?
No, not all plasma cutters require an air compressor. Some plasma cutters are designed to use a shop air compressor, while others are designed to use a built-in compressor. The type of plasma cutter you choose will depend on the type of material you are cutting and the thickness of the material. If you are cutting thin materials, such as sheet metal, then a shop air compressor may be sufficient. However, if you are cutting thicker materials, such as steel, then a built-in compressor may be necessary. Additionally, some plasma cutters are designed to be used with a combination of shop air and a built-in compressor. Ultimately, the type of plasma cutter you choose will depend on the type of material you are cutting and the thickness of the material.
Can you use a plasma cutter to heat metal?
Yes, you can use a plasma cutter to heat metal. A plasma cutter is a tool that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials, such as metal. The plasma cutter works by creating an electrical arc between an electrode and the metal being cut. This arc is then used to heat the metal to a very high temperature, allowing it to be cut. The plasma cutter is a very versatile tool and can be used to cut through a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. It can also be used to heat metal for welding, brazing, and other metalworking processes. The plasma cutter is a great tool for cutting and heating metal, and it can be used in a variety of applications.
How much does a CNC router cost?
The cost of a CNC router can vary greatly depending on the size, type, and features of the machine. Generally, a small hobbyist CNC router can cost anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000, while a larger industrial-grade CNC router can cost anywhere from $20,000 to $100,000 or more. The cost of a CNC router also depends on the type of materials it is designed to work with, as well as the type of software and accessories that come with the machine. For example, a CNC router designed to work with wood may cost less than one designed to work with metal. Additionally, the cost of a CNC router can be affected by the type of control system it uses, such as a computer numerical control (CNC) system or a manual control system. Finally, the cost of a CNC router can be affected by the type of maintenance and support services that come with the machine.