Machining movements refer to the various motions that a cutting tool can make when performing a machining operation. These motions are typically used to shape a workpiece by removing material from it. The most common machining movements are linear, circular, and helical. Linear movements involve the cutting tool moving in a straight line, while circular movements involve the cutting tool moving in a circular path. Helical movements involve the cutting tool moving in a spiral pattern. Each of these movements can be used to create different shapes and features on a workpiece.
Linear movements are typically used for straight cuts, such as those used to create grooves or slots. Circular movements are used to create curved surfaces, such as those used to create holes or contours. Helical movements are used to create helical shapes, such as those used to create threads.
In addition to these basic machining movements, there are also more complex movements that can be used to create more intricate shapes and features. These include taper, contour, and spiral movements. Taper movements involve the cutting tool moving in a tapered pattern, while contour movements involve the cutting tool moving in a curved pattern. Spiral movements involve the cutting tool moving in a spiral pattern.
Each of these machining movements can be used to create different shapes and features on a workpiece. The type of movement used will depend on the desired shape or feature that needs to be created. It is important to understand the different machining movements and how they can be used to create the desired shape or feature.
What are machining processes?
Machining processes are a type of manufacturing process that involve the use of specialized tools and machines to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Machining processes are used to create parts for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products. The most common machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and sawing.
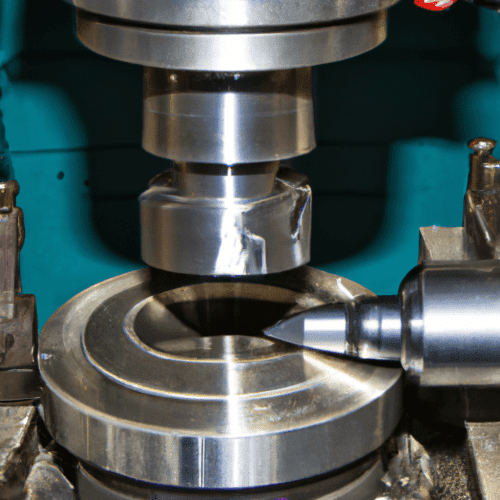
Turning is a machining process that involves rotating a workpiece on a lathe while a cutting tool is used to remove material from the workpiece. This process is used to create cylindrical parts with a uniform diameter and shape.
Milling is a machining process that involves using a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. This process is used to create flat surfaces, slots, and grooves in a workpiece.
Drilling is a machining process that involves using a rotating drill bit to create holes in a workpiece. This process is used to create holes for fasteners, such as screws and bolts.
What are the three main movements of turning operations?
Turning operations are a type of machining process used to shape and finish a workpiece by removing material from the surface. The three main movements of turning operations are the cutting tool’s feed, the cutting tool’s rotation, and the workpiece’s rotation.
The feed movement is the linear motion of the cutting tool along the workpiece’s surface. This motion is usually controlled by a feed rate, which is the distance the cutting tool moves in a given amount of time. The feed rate is typically measured in inches per minute (IPM).
The cutting tool’s rotation is the rotational motion of the cutting tool around its own axis. This motion is usually controlled by a spindle speed, which is the rotational speed of the cutting tool in revolutions per minute (RPM).
What machining means?
Machining is a manufacturing process in which a material is cut into a desired shape and size using a variety of tools. It is a subtractive process, meaning that material is removed from the workpiece in order to achieve the desired shape and size. Machining is used to create parts for a wide variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
The most common machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and sawing. Turning is the process of cutting a cylindrical shape from a workpiece, usually using a lathe. Milling is the process of cutting a flat surface on a workpiece, usually using a milling machine. Drilling is the process of creating a hole in a workpiece, usually using a drill press. Grinding is the process of removing material from a workpiece using an abrasive wheel. Sawing is the process of cutting a workpiece into two or more pieces, usually using a saw.
What is another word for machining?
Machining is a process of shaping and cutting materials to create a desired product. It is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which is the opposite of additive manufacturing. Another word for machining is metalworking, which is the process of working with metals to create a desired product. Metalworking includes machining, as well as other processes such as forging, casting, and welding. Metalworking is a broad term that encompasses many different processes, and machining is just one of them.
What are commonly used machining operations?
Machining operations are a type of manufacturing process that involve the use of specialized tools and machines to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Common machining operations include turning, drilling, milling, grinding, sawing, and broaching.
Turning is a machining process that involves rotating a workpiece on a lathe to shape and cut it into a desired shape. It is used to create cylindrical parts with smooth surfaces. Drilling is a machining process that involves using a drill bit to create a hole in a workpiece. It is used to create holes of various sizes and depths. Milling is a machining process that involves using a milling machine to shape and cut a workpiece. It is used to create complex shapes and features on a workpiece. Grinding is a machining process that involves using an abrasive wheel to shape and cut a workpiece. It is used to create smooth surfaces and remove material from a workpiece.
What are the basic elements of machining?
Machining is a manufacturing process that involves the use of specialized tools and machines to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The basic elements of machining include cutting tools, workpiece, machine tool, and cutting fluids.
Cutting tools are the tools used to shape and cut the material. These tools can be made from a variety of materials such as high-speed steel, carbide, and ceramics. The type of cutting tool used depends on the material being machined and the desired shape and size of the finished product.
The workpiece is the material that is being machined. This can be a variety of materials such as metals, plastics, composites, and ceramics. The workpiece is held in place by a workholding device such as a vise, chuck, or fixture.
The machine tool is the machine that is used to shape and cut the material. This can be a variety of machines such as lathes, milling machines, drill presses, and grinders.
What are tools and machines?
Tools and machines are devices used to perform a specific task or set of tasks. Tools are typically hand-held and are used to perform a single task, such as a hammer for pounding nails or a saw for cutting wood. Machines, on the other hand, are typically larger and more complex, and are used to perform multiple tasks, such as a car for transportation or a computer for data processing. Tools and machines are used in a variety of industries, from construction to manufacturing to agriculture.
Tools and machines are used to increase efficiency and productivity, as they can perform tasks faster and more accurately than humans. They can also be used to reduce the amount of physical labor required to complete a task, allowing people to focus on more complex tasks. Additionally, tools and machines can be used to increase safety, as they can reduce the risk of injury or death due to human error.
Tools and machines come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and can be powered by a variety of sources, such as electricity, gas, or manual labor.
What is traditional machining process?
Traditional machining processes are a set of manufacturing techniques used to shape and finish components by removing material from a workpiece. These processes are typically used to produce parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances. Traditional machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and sawing.
Turning is a machining process used to produce cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool is fed into it. The cutting tool is typically a single-point cutting tool, but can also be a multi-point cutting tool. The cutting tool is held in a tool holder and is fed into the rotating workpiece. The cutting tool removes material from the workpiece in the form of chips.
Milling is a machining process used to produce flat and complex shapes. It is similar to turning, but instead of a single-point cutting tool, a multi-point cutting tool is used. The cutting tool is held in a spindle and is fed into the workpiece. The cutting tool removes material from the workpiece in the form of chips.