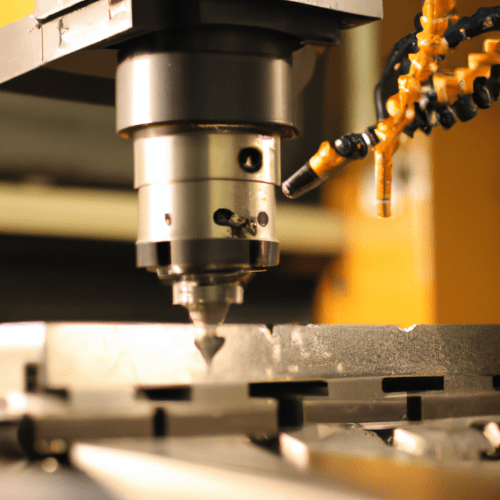
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a process used in the manufacturing industry that employs computerized controls and specialized software to automate the movement of tools and machinery. The process involves the use of a computer-controlled milling machine to cut and shape materials into a desired shape or form. The milling machine is equipped with a cutting tool, such as a drill bit, that is programmed to move in a specific pattern and direction. The cutting tool is then used to cut away material from the workpiece, creating the desired shape or form.
The CNC milling process begins with the creation of a computer-aided design (CAD) file. This file contains the instructions for the cutting tool, including the type of material to be cut, the size and shape of the desired product, and the cutting path. Once the CAD file is created, it is sent to the CNC milling machine, which is programmed to follow the instructions in the file. The machine then moves the cutting tool along the cutting path, cutting away material from the workpiece to create the desired shape or form.
The CNC milling process is highly accurate and can produce complex shapes and forms with a high degree of precision. It is also a relatively fast process, allowing for the production of large quantities of parts in a short amount of time. Additionally, CNC milling is a cost-effective process, as it requires minimal manual labor and can be used to produce a wide variety of parts.
How does the process of milling work?
Milling is a process used to shape and cut materials, such as metal and wood, by feeding a workpiece through a rotating cutting tool. The cutting tool is typically a multipoint cutting tool, such as a milling cutter, which rotates about an axis that is perpendicular to the workpiece. The cutting tool is fed into the workpiece in a linear direction, and the cutting tool removes material from the workpiece in a series of small cuts.
The cutting tool is typically made of a hard material, such as high-speed steel or carbide, and is designed to cut through the material with minimal wear and tear. The cutting tool is usually held in a spindle, which is a rotating shaft that is connected to a motor. The motor is used to rotate the cutting tool at a high speed, which allows it to cut through the material quickly and efficiently.
The cutting tool is fed into the workpiece at a predetermined depth and speed. The depth of the cut is determined by the size of the cutting tool and the speed of the motor.
What are the basics of CNC milling?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a machining process that uses computer-controlled cutting tools to shape a workpiece. It is a type of subtractive manufacturing process, where material is removed from a workpiece to create a desired shape or finish. CNC milling is a versatile process that can be used to create a wide variety of shapes and features, from simple to complex.
The basic components of a CNC milling machine include the cutting tool, the workpiece, the spindle, the table, and the controller. The cutting tool is the part of the machine that actually cuts the material. It is usually a rotating cutting tool, such as an end mill or drill bit. The workpiece is the material that is being machined. The spindle is the part of the machine that holds and rotates the cutting tool. The table is the part of the machine that holds the workpiece in place. The controller is the part of the machine that controls the movement of the cutting tool and the speed of the spindle.
What is CNC machining and how does it work?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control (CNC) machines to shape and cut materials into a desired shape or size. CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process, meaning that material is removed from a workpiece to create the desired shape or size. CNC machining is used to create parts for a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products.
CNC machining works by using a computer program to control the movement of the machine’s cutting tools. The program is written in a language called G-code, which is a numerical code that tells the machine what to do. The program is loaded into the machine’s memory and the machine is then ready to begin machining.
The CNC machine is equipped with a variety of cutting tools, such as drills, end mills, and reamers. The cutting tools are mounted on a spindle, which is driven by a motor.
Do CNC machines require any programming?
Yes, CNC machines do require programming. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, and the programming is what allows the machine to be controlled by a computer. The programming is typically done using a language called G-code, which is a numerical control programming language. G-code is used to tell the machine what type of motion to perform, what speed to move at, and what tools to use. The programming also includes instructions for the machine to follow in order to produce the desired output. Depending on the complexity of the job, the programming can be done manually or with the help of a computer-aided design (CAD) program. In either case, the programming must be done correctly in order for the machine to produce the desired results.
What is G code in CNC?
G code is a programming language used to control automated machine tools such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. It is a language that is used to tell the machine what to do and how to do it. G code is used to create a program that will control the machine’s movements and operations. It is a language that is used to create a set of instructions that the machine can understand and execute. G code is used to control the motion of the machine, the speed of the machine, the feed rate, the cutting tool, and other aspects of the machine’s operation. G code is also used to control the machine’s spindle speed, coolant, and other machine functions. G code is a language that is used to create a program that will control the machine’s movements and operations. It is a language that is used to create a set of instructions that the machine can understand and execute.
How is CNC machine controlled?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are controlled by a computer program that is written in a specific language. The program is loaded into the machine’s memory and then the machine is instructed to execute the program. The program contains instructions for the machine to move the cutting tool in a specific direction, at a specific speed, and with a specific amount of force. The program also contains instructions for the machine to adjust the cutting tool’s position and orientation in order to create the desired shape. The program can also be used to control the speed and force of the cutting tool, as well as the speed and force of the machine itself. The program can also be used to control the temperature of the cutting tool, as well as the temperature of the machine itself. The program can also be used to control the amount of lubrication that is used on the cutting tool, as well as the amount of lubrication that is used on the machine itself.
How does a CNC lathe machine work?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe machine is a type of automated lathe that is controlled by a computer program. It is used to produce precise parts with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability. The CNC lathe machine works by taking a blank piece of material, such as metal or wood, and using a cutting tool to shape it into the desired shape. The cutting tool is mounted on a spindle that is driven by a motor. The motor is controlled by a computer program that is programmed with the desired shape and dimensions of the part.
The CNC lathe machine is programmed with a series of instructions that tell the machine how to move the cutting tool and the material in order to create the desired shape. The instructions are written in a language called G-code, which is a standard language used by CNC machines. The instructions tell the machine how to move the cutting tool in relation to the material, as well as how fast to move it and how deep to cut.