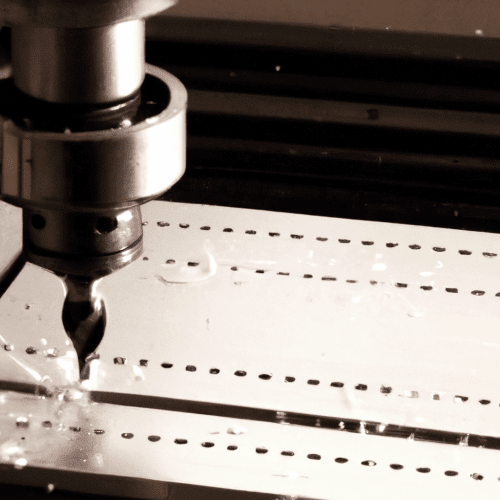
Milling is a process used in the manufacturing industry that involves the cutting and shaping of a material, such as metal or wood, into a specific shape or form. It is typically done using a machine called a milling machine, which uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece. The cutting tool is usually a multi-point cutting tool, such as a drill bit, end mill, or router bit. The cutting tool is moved in a linear direction along the surface of the workpiece, while the workpiece is held in place by a vise or other clamping device. The cutting tool is then rotated at a high speed, and the cutting edges of the tool interact with the material of the workpiece to remove material in the form of chips. The chips are then collected and disposed of, or recycled for other uses. The shape of the workpiece is determined by the shape of the cutting tool, and the size and shape of the cut can be adjusted by changing the speed and feed rate of the cutting tool. Milling is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics, and is used to create a wide range of products, from medical implants to car parts.
How does a milling machine operate?
A milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials such as metal and wood. It uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece in a variety of directions. The cutting tool can be moved in multiple directions and the workpiece can be moved in multiple directions to create a variety of shapes and sizes.
Milling machines typically consist of a spindle, which rotates the cutting tool, and a table, which is used to hold the workpiece. The spindle is powered by an electric motor, which is connected to a gearbox that controls the speed and direction of the spindle. The table is usually moved by a hand crank or a motor.
The cutting tool is usually a rotating cutting tool such as an end mill, drill bit, or router bit. The cutting tool is held in a collet, which is a type of chuck that holds the cutting tool in place. The cutting tool is then moved in a variety of directions to cut away material from the workpiece.
What are the steps of the milling process?
Milling is a machining process that uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. The milling process involves several steps, each of which requires careful planning and execution.
The first step in the milling process is to select the appropriate tool for the job. This includes selecting the type of milling cutter, the cutting speed, the feed rate, and the depth of cut. Once the tool has been selected, the workpiece must be securely clamped to the milling machine table.
The next step is to set the cutting parameters. This includes setting the spindle speed, the feed rate, and the depth of cut. The cutting parameters must be set to ensure that the cutting tool does not overheat or cause excessive wear.
Once the cutting parameters have been set, the milling process can begin. The cutting tool is moved across the workpiece in a series of passes. Each pass removes a small amount of material from the workpiece. The depth of each pass is determined by the cutting parameters that were set earlier.
How does plain milling works?
Plain milling, also known as surface milling or slab milling, is a process used to create flat surfaces on a workpiece. It is typically used to machine large, flat surfaces, such as the top of a table or a side of a block. The process involves a rotating cutter that moves along the surface of the workpiece in a linear direction, removing material as it goes. The cutter is usually a multi-toothed end mill, but can also be a single-toothed end mill or a face mill.
The cutter is held in a spindle, which is connected to a motor that rotates the cutter at a predetermined speed. The speed of the cutter is determined by the material being machined and the desired finish. The feed rate, or the rate at which the cutter moves along the surface of the workpiece, is also determined by the material and the desired finish.
What is the milling process in manufacturing?
Milling is a manufacturing process that involves the use of rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. It is a versatile process that can produce a variety of features on a part by cutting away excess material. The milling process can be used to create flat surfaces, contoured surfaces, angled surfaces, slots, pockets, and complex 3D shapes.
The milling process begins with the selection of the appropriate cutting tool for the job. The cutting tool is then mounted on a spindle, which is connected to a motor that rotates the cutting tool at a high speed. The cutting tool is then moved across the workpiece in a specific pattern, removing material as it moves. The depth of the cut and the speed of the cutting tool can be adjusted to achieve the desired result.
The milling process can be used to create a variety of features on a part, including flat surfaces, contoured surfaces, angled surfaces, slots, pockets, and complex 3D shapes. The milling process can also be used to create threads, grooves, and other features.
What is the difference between grinding and milling?
Milling and grinding are two common machining processes performed in the manufacturing industry. They both involve the removal of material from a workpiece, and they both support a wide variety of materials, such as metal, wood, plastics, and ceramics. However, the two processes are distinct in their execution and results.
Milling is a cutting process that uses a milling cutter to remove material from the surface of a workpiece. The milling cutter is a rotary cutting tool with multiple cutting points. As the milling cutter rotates, the cutting points on the tool repeatedly cut into and exit from the material, removing chips of material in the process. Milling can be used to create a variety of features on a part, including slots, pockets, and contours.
Grinding is an abrasive machining process that uses a grinding wheel as the cutting tool. A grinding wheel is a wheel composed of an abrasive compound and used for various grinding (abrasive cutting) and abrasive machining operations.
Why is milling used?
Milling is a machining process used to shape and finish materials such as metals, plastics, and wood. It is one of the most commonly used processes in industry and machine shops today. Milling can be used to create a variety of features on a part by cutting away excess material in order to produce a desired shape. It can also be used to create a variety of holes, slots, and other features.
Milling is used for a variety of reasons. It is a fast and efficient way to produce parts with complex shapes and features. It is also a very precise process, allowing for tight tolerances and repeatability. Milling can also be used to produce parts with a high degree of accuracy and surface finish. Additionally, milling can be used to produce parts with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
Milling is also a versatile process, allowing for a variety of operations to be performed on a single part. This includes operations such as drilling, tapping, reaming, and counterboring.
Which type of mechanism is used in milling machine?
Milling machines use a variety of different types of mechanisms to move and control the cutting tool. The most common type of mechanism used in milling machines is the geared drive mechanism. This type of mechanism uses a series of gears to transfer power from the motor to the spindle, allowing the cutting tool to move in a precise and controlled manner. Other types of mechanisms used in milling machines include belt drives, rack and pinion drives, and leadscrew drives. Each type of mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to choose the right type of mechanism for the job.
What is milling machine operation parts and types?
A milling machine is a machine tool used for the shaping of metal and other solid materials. Its basic form is that of a rotating cutter or endmill which rotates about the spindle axis (similar to a drill), and a movable table to which the workpiece is affixed. Milling operations involve the movement of the rotating cutter across the workpiece in order to shape it or produce features such as slots, pockets, and contours.
The main parts of a milling machine are the base, column, knee, saddle, table, overarm, spindle, arbor, and cutter. The base is the foundation of the machine and is mounted to the floor. The column is the main supporting frame mounted vertically on the base. The knee is a vertical adjustment mounted on the column, which allows the table to be moved up and down. The saddle is a platform that supports the table and is mounted on the knee. The table is the work surface and is mounted on the saddle. The overarm is a horizontal arm mounted on the column, which supports the arbor.
What are the general operation of the CNC milling machine?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling machine is a type of machining tool that uses computer-controlled commands to cut and shape materials. It is a versatile tool that can be used to create a variety of shapes and sizes, from simple to complex. The CNC milling machine is composed of several components, including a spindle, a table, a cutting tool, and a computer-controlled system.
The spindle is the main component of the CNC milling machine and is responsible for rotating the cutting tool. The spindle is connected to the computer-controlled system, which is responsible for controlling the speed and direction of the spindle. The table is the platform on which the material is placed and is used to hold the material in place while the cutting tool is used to shape the material.
The cutting tool is the part of the CNC milling machine that is responsible for cutting the material. It is usually a rotating tool, such as a drill bit, end mill, or router bit.