Grinding and milling are both material removal processes used in manufacturing, but they differ significantly in their methods and applications. Grinding involves using abrasive particles or wheels to remove material from a workpiece, typically achieving finer finishes and tighter tolerances. It’s often used for hardened materials or when high precision is required. Milling, on the other hand, uses rotating cutting tools with multiple edges to remove material from a workpiece. It’s more versatile, capable of creating a wide range of shapes and features, and is generally faster for bulk material removal.
Grinding is usually a finishing process, while milling can be used for both roughing and finishing operations. The choice between grinding and milling depends on factors such as the material being worked, the desired surface finish, the complexity of the part, and the required precision. Grinding excels at producing extremely smooth surfaces and maintaining tight dimensional tolerances, while milling offers greater flexibility in creating complex geometries and is more efficient for larger-scale material removal.
- Grinding and milling are machining processes used for material removal.
- Grinding uses abrasive particles on a grinding wheel to remove material and polish surfaces.
- Milling uses rotating cutting blades to scrape off material from a workpiece.
- The choice between grinding and milling depends on factors such as the material being worked and the desired outcome.
- Both processes have their advantages and are widely used in various industries.
What is Milling?
Milling is a machining process that involves the use of a milling machine to remove material from a workpiece. The milling machine has cutting blades that rotate and press against the workpiece, scraping off material as the cutting tool moves across the surface.
There are two types of milling: face milling and peripheral milling. Face milling involves cutting at the corners of the cutting tool, while peripheral milling involves cutting around the circumference of the tool. This process is commonly used for cutting deep slots and gear teeth.
Table: Types of Milling
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Face Milling | Used to create flat surfaces and flat-bottomed cavities |
| Peripheral Milling | Used for cutting deep slots, threads, and gear teeth |
During the milling process, the workpiece is securely held in place to ensure accurate and precise machining. This allows for the creation of complex shapes and features on the workpiece, making milling a versatile machining technique.
What is Grinding?
Grinding is a machining process that involves the use of a grinding wheel to remove material from a workpiece. The grinding wheel is made up of abrasive particles that rub against the workpiece, wearing away material and polishing the surface. This process is commonly used in industries such as metalworking, woodworking, and manufacturing, where precision and surface finishing are crucial.
During the grinding process, the grinding wheel rotates at high speed while pressing against the workpiece surface. The abrasive particles on the wheel gradually remove material, creating the desired shape or surface finish. Different types of grinding techniques can be employed, depending on the specific application. These include surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, and centerless grinding, among others.
Grinding Process
The grinding process begins with the selection of the appropriate grinding wheel for the task at hand. The grinding wheel composition can vary based on the material being worked and the desired outcome. For example, grinding wheels made of silicon carbide are ideal for grinding non-ferrous metals, while alumina ceramic wheels are better suited for grinding steel. Once the wheel is chosen, it is mounted on a grinding machine, which provides the necessary rotational movement.
During the grinding process, the workpiece is held securely in place while the grinding wheel is brought into contact with the surface to be ground. The grinding wheel’s abrasive particles remove material from the workpiece through a combination of rubbing and cutting actions. The grinding process can be used to remove excess material, shape the workpiece, or achieve a desired surface finish. It is a versatile machining process that can be applied to various materials, from metals to composites.
Overall, grinding is an essential process in many industries, providing a precise and efficient means of material removal and surface finishing. With the right grinding wheel and machine setup, manufacturers can achieve the desired results, whether it’s removing excess material or achieving a smooth, polished surface.
Grinding Wheel
A grinding wheel is an essential tool used in the grinding process. It consists of abrasive particles that are bonded together to form a solid, circular shape. The choice of grinding wheel depends on the material being machined and the desired outcome. Different types of grinding wheels are available in the market, each designed for specific applications.
One commonly used material for grinding wheels is silicon carbide. It is a hard and sharp abrasive that is suitable for grinding materials such as cast iron, non-ferrous metals, and non-metallic materials. Another popular material is alumina ceramic, which provides a high level of hardness and is ideal for grinding steel, hardened steels, and high-speed steels. Zirconia alumina is another type of grinding wheel material that offers excellent grit retention and is commonly used for grinding stainless steel and other heat-treated metals.
During the grinding process, fluids are often used to cool and lubricate the grinding wheel and workpiece. The fluids help to prevent overheating and improve the overall efficiency of the grinding operation. Furthermore, the fluids also aid in removing the chips produced during grinding, preventing them from clogging the grinding wheel and reducing its effectiveness.
| Grinding Wheel Material | Main Applications |
|---|---|
| Silicon carbide | Cast iron, non-ferrous metals, non-metallic materials |
| Alumina ceramic | Steel, hardened steels, high-speed steels |
| Zirconia alumina | Stainless steel, heat-treated metals |
Milling Operations
There are different types of milling operations that can be performed using a milling machine. Each operation serves a specific purpose and is used to achieve different outcomes. Here are some common types of milling operations:
Face Milling
Face milling is a type of milling operation that is used to create flat surfaces on the workpiece. The cutting tool used in face milling has multiple cutting edges and cuts across the workpiece to remove material and create a flat surface.
Peripheral Milling
Peripheral milling is another type of milling operation that involves cutting around the circumference of the cutting tool. This operation is commonly used for cutting deep slots, threads, and gear teeth. The cutting tool moves along the edges of the workpiece to remove material and create the desired shape.
Conventional Milling
In conventional milling, the workpiece is fed against the rotation of the milling cutter. This type of milling operation is commonly used for roughing operations as it allows for a higher material removal rate. However, it can result in a less smooth surface finish.
Climb Milling
In climb milling, the workpiece is fed in the same direction as the rotation of the milling cutter. This type of milling operation is commonly used for finishing operations as it produces a smoother surface finish. It also reduces the chances of workpiece chatter and provides better tool life.
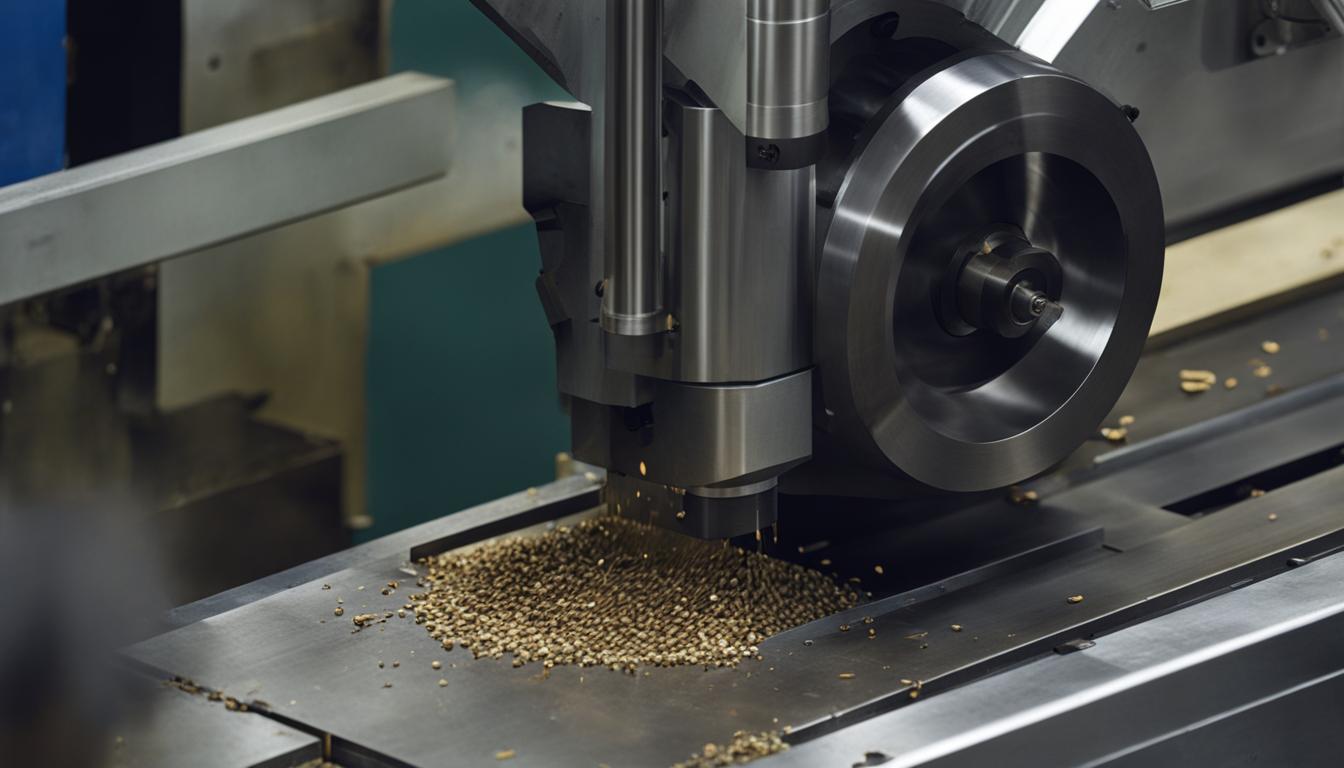

Overall, the choice of milling operation depends on the desired outcome and the type of surface or feature that needs to be machined. Each operation has its advantages and considerations, and selecting the appropriate operation is crucial to achieving the desired results in milling processes.
Grinding Applications
Grinding is a versatile machining process that finds applications in various industries. It is primarily used for material removal from a workpiece or polishing its surface to achieve a smooth finish. The process involves the use of a grinding wheel with abrasive particles that rub against the workpiece, wearing away material and refining the surface. Let’s explore some common applications of grinding in different industries.
Metalworking
In the metalworking industry, grinding is widely used for shaping and smoothing metal surfaces. It is commonly employed to remove excess material, such as burrs or welds, and to create precise shapes and dimensions. Grinding can be performed on a range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Woodworking
In woodworking, grinding is utilized to smooth wooden surfaces and remove imperfections. It is often used in the preparation of wooden furniture and crafts, where achieving a polished and flawless surface is essential. Grinding can help in leveling uneven wood, removing blemishes, and providing a smooth finish.
Other Industries
Grinding also finds applications in various other industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. In the automotive industry, for example, grinding is used to refine the surface of engine components for improved performance. In the aerospace industry, grinding can be employed for precision machining of turbine blades and other critical parts. In electronics manufacturing, grinding is used for surface finishing of electronic components.
Overall, grinding is a versatile machining process that plays a crucial role in material removal and surface polishing across different industries. Its ability to remove excess material and polish surfaces makes it an essential technique in manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Milling Machines
Milling machines are essential tools used in the manufacturing industry to perform milling operations. These machines come in different types and are designed to efficiently remove material from a workpiece using cutting blades. With the workpiece securely fixed in place, the milling machine’s cutting blades rotate against the workpiece, allowing for precise and controlled material removal.
The types of milling machines include vertical milling machines, horizontal milling machines, and universal milling machines. Vertical milling machines have a vertical spindle that allows for the cutting tool to move up and down, while horizontal milling machines have a horizontal spindle for side-to-side cutting. Universal milling machines combine both vertical and horizontal spindles, offering greater versatility for various milling operations.
The cutting blades used in milling machines can be customized to suit the specific machining requirements. Different types of cutting blades are available, including end mills, face mills, and slotting cutters. These blades have different shapes and designs, allowing for the creation of various features on the workpiece, such as holes, slots, pockets, and contours.
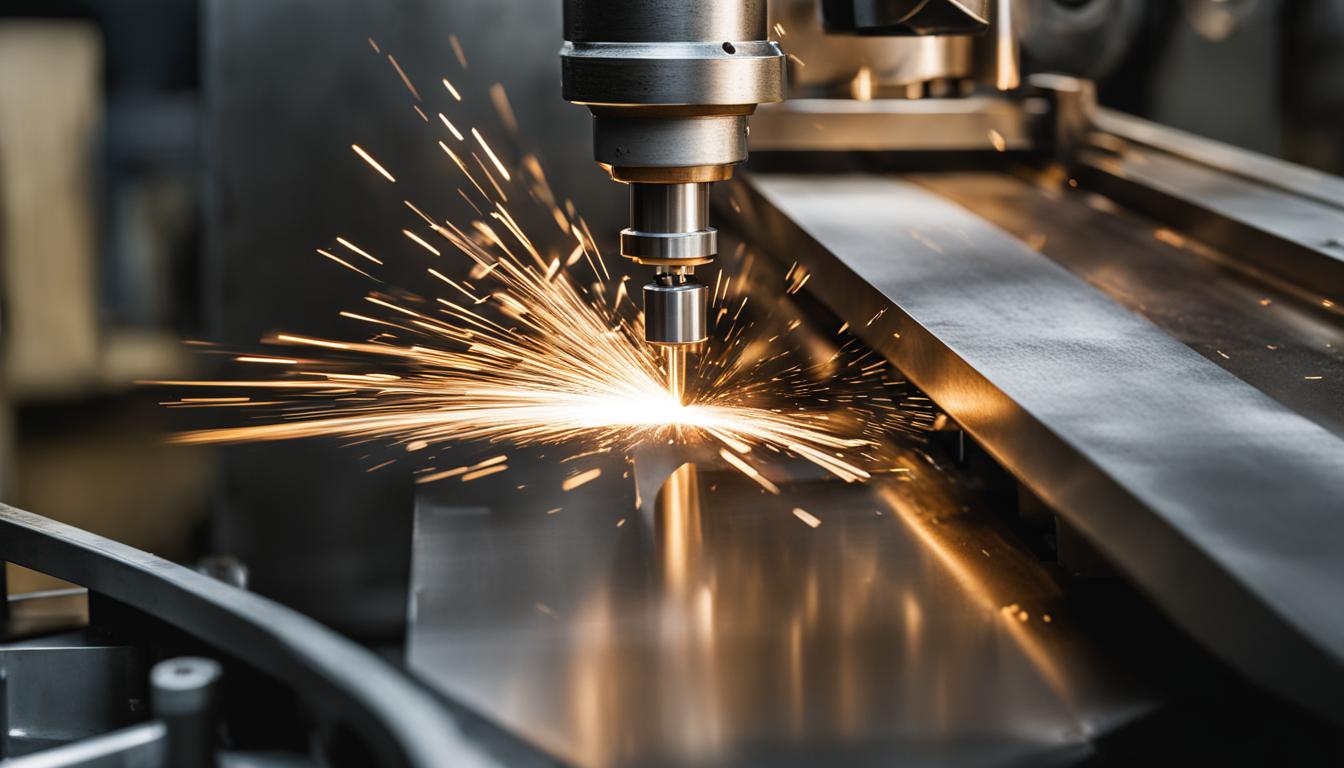

| Type of Milling Machine | Description |
|---|---|
| Vertical Milling Machine | A milling machine with a vertical spindle for up and down cutting. |
| Horizontal Milling Machine | A milling machine with a horizontal spindle for side-to-side cutting. |
| Universal Milling Machine | A milling machine that combines both vertical and horizontal spindles for enhanced versatility. |
With the wide range of milling machines available, manufacturers can choose the most suitable machine for their specific application, ensuring efficient and accurate milling operations.
Grinding Machines
Grinding machines are essential tools in the machining industry, used to remove material from a workpiece and achieve a desired surface finish. There are several types of grinding machines, each designed for specific applications and materials. Let’s explore some of the common types:
Cylindrical Grinding Machines
Cylindrical grinding machines are used to grind cylindrical surfaces of a workpiece. They consist of a rotating grinding wheel and a workpiece holder. The workpiece is rotated while the grinding wheel moves back and forth, removing material and creating the desired shape and finish.
Surface Grinding Machines
Surface grinding machines are used to grind flat surfaces of a workpiece. They have a horizontal grinding wheel that moves across the workpiece, removing material and achieving a smooth surface finish. Surface grinding machines are commonly used in manufacturing industries for precision grinding.
Internal Grinding Machines
Internal grinding machines are used to grind the internal diameter of a workpiece. They have a small grinding wheel that rotates inside the workpiece, removing material and creating precise internal features. Internal grinding machines are commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries for precision machining.
| Types of Grinding Machines | Applications |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Grinding Machines | Used for grinding cylindrical surfaces of a workpiece |
| Surface Grinding Machines | Used for grinding flat surfaces of a workpiece |
| Internal Grinding Machines | Used for grinding the internal diameter of a workpiece |
These are just a few examples of grinding machines available in the industry. Each type of machine has its own advantages and limitations, making it suitable for specific applications. By choosing the right grinding machine and grinding wheel, manufacturers can achieve precise material removal and surface finishing, leading to high-quality products.
Advantages of Milling
Milling offers several advantages as a machining process. One of the key benefits is the ability to add features to an already machined workpiece. This makes milling a valuable secondary machining technique in manufacturing. By using cutting blades that rotate and scrape off material, milling machines can easily create holes, slots, pockets, and contours with precision and accuracy.
Another advantage of milling is its versatility. Milling machines can handle a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics and composites. This makes them suitable for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Whether it’s roughing or finishing operations, milling machines can consistently deliver the desired results.
In addition, milling machines offer excellent control over the machining process. Operators can adjust the speed, feed rate, and depth of cut to achieve the desired outcome. This level of control allows for efficient material removal and ensures the workpiece is machined according to specifications.
Advantages of Milling
- Ability to add features to an already machined workpiece
- Versatility in handling various materials
- Precision and accuracy in machining
- Control over machining parameters
Overall, milling is a versatile and reliable machining technique that offers numerous advantages. Its ability to add features, versatility in material handling, and precise control make it a preferred choice for many manufacturing applications.
Advantages of Grinding
Grinding offers several advantages in the machining process. One of the key benefits is its ability to remove large amounts of material from a workpiece, making it suitable for roughing operations. Whether it’s shaping metal surfaces, removing welds, or sharpening cutting tools, grinding excels at material removal. Additionally, grinding can be used to achieve a smooth, polished surface finish.
The versatility of grinding is another advantage. It can be employed with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and wood. This makes it a valuable process in various industries, from automotive and aerospace to construction and woodworking. Grinding machines are widely available and can be used for both small-scale and large-scale applications.
In summary, grinding provides significant advantages in terms of material removal and surface finishing. Its ability to remove large amounts of material and achieve a smooth surface makes it a versatile machining process suitable for various industries and applications.
Advantages of Grinding:
- Effective in removing large amounts of material
- Can achieve a smooth surface finish
- Versatile process suitable for various materials
- Widely available grinding machines for different applications
Comparison of Grinding and Milling
Grinding and milling are two popular machining processes used in the manufacturing industry. While both processes involve material removal from a workpiece, there are distinct differences between grinding and milling. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate machining process for specific applications.
Grinding is a process that utilizes a grinding wheel with abrasive particles to remove material and polish surfaces. It is commonly used for precision machining and achieving a smooth finish. On the other hand, milling involves the use of rotating cutting blades to scrape off material from the workpiece. This process is versatile and can add features like holes, slots, pockets, and contours to a machined workpiece.
One key difference between grinding and milling is the nature of the tool used. Grinding utilizes a grinding wheel, while milling employs cutting blades. Additionally, the materials being worked and the desired outcome also play a role in selecting the most suitable process. Grinding is effective for removing larger amounts of material, while milling offers precision and the ability to add features to the workpiece.
| Grinding | Milling |
|---|---|
| Utilizes a grinding wheel with abrasive particles | Uses rotating cutting blades |
| Primarily used for removing material and polishing surfaces | Can add features like holes, slots, pockets, and contours |
| Effective for removing larger amounts of material | Offers precision and the ability to add features |
In summary, grinding and milling are distinct machining processes with different tools and techniques. Grinding employs abrasive particles on a grinding wheel for material removal and surface polishing, whereas milling uses rotating cutting blades to scrape off material and add features. The choice between grinding and milling depends on factors such as the material being worked and the desired outcome, making it essential to understand their differences for optimal machining results.
Conclusion
The difference between grinding and milling lies in their respective methods of material removal. Grinding utilizes a grinding wheel with abrasive particles to rub away material and achieve a polished surface. On the other hand, milling employs a milling machine equipped with rotating cutting blades to scrape off material from the workpiece.
Both grinding and milling have their advantages and are widely used in various industries. Grinding is particularly effective for removing large amounts of material and achieving a smooth finish. It can be used with different materials and is available in various specialized grinding machines. Milling, on the other hand, offers precise and accurate machining, making it suitable for adding features to already machined workpieces.
Understanding the difference between grinding and milling is crucial for selecting the appropriate machining process for specific applications. Factors such as the material being worked, the desired outcome, and the available equipment should be considered. By choosing the right method, manufacturers can achieve optimal results in their manufacturing processes.