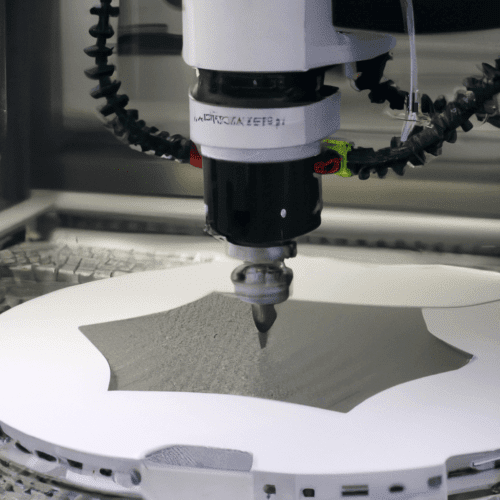
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) prototyping has sparked a revolutionary transformation in the process of product conceptualization, design, and production. The widespread adoption of this technology has significantly impacted numerous industries, such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, consumer electronics, and beyond.
The Roots of CNC Prototyping
CNC prototyping’s origins can be traced back to the mid-20th century, a time when manual machining processes prevailed as the standard practice. Manual machining involved skilled operators manipulating machine tools manually to cut, shape, and drill materials into specific forms. Although dependable, this method had certain drawbacks concerning accuracy, speed, and consistency.
The Emergence of Numerical Control
The first significant step towards CNC prototyping came with the development of Numerical Control in the 1940s and 1950s. Numerical Control was a method that utilized punched cards or tapes to control the movements of machine tools. This innovation allowed engineers and manufacturers to program a sequence of instructions, enabling the machines to produce precise and complex parts with higher accuracy than traditional manual techniques.
Early CNC Prototyping
During the 1960s, a notable advancement emerged with the transition from Numerical Control to Computer Numerical Control. CNC allowed manufacturers to use computers to control machine tools, replacing the cumbersome punched cards with more sophisticated computer programs. This advancement greatly improved the flexibility and efficiency of prototyping and production processes.
CNC prototyping made its debut in industries like aerospace and defense, where the need for complex and intricate parts was high. The technology also began to find its way into automotive and electronics manufacturing, revolutionizing these sectors and setting the stage for further advancements.
Advancements in CNC Technology
The 1980s marked a period of rapid growth and innovation in CNC prototyping. As computer technology improved, CNC machines became more powerful and versatile. The integration of CAD and CAM software alongside CNC systems has given designers and engineers the ability to create 3D models and effortlessly convert them into machine code. This seamless integration improved the design-to-production workflow, reducing errors and saving valuable time.
In the 1990s, there were remarkable advancements, notably the emergence of multi-axis CNC machines. These cutting-edge machines had the capability to move in multiple directions concurrently, unlocking the potential for crafting intricate geometries that were once impossible with conventional machining techniques. Furthermore, the integration of CNC milling, turning, and laser cutting techniques broadened the spectrum of materials applicable, encompassing metals, plastics, and even composite materials.
The Rise of Rapid Prototyping
The onset of the 21st century marked the remarkable rise of rapid prototyping technologies, including pioneering 3D printing and cutting-edge additive manufacturing. These groundbreaking technologies have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, opening up limitless possibilities for designers, engineers, and innovators. With their unparalleled ability to create intricate and complex objects layer by layer, 3D printing and additive manufacturing have catapulted product development into a new era of efficiency and creativity. This unprecedented progress has not only streamlined production processes but has also empowered entrepreneurs and researchers to bring their wildest ideas to life with astounding ease. As the world embraces these innovative advancements, we find ourselves on the brink of a profound transformation that will undoubtedly shape the future of manufacturing and usher in a new era of technological wonders.
CNC Prototyping Today
CNC prototyping continues to thrive, continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible in product design and development. The integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies has enabled “smart” CNC systems capable of real-time monitoring, self-optimization, and predictive maintenance.
The adoption of CNC in small-scale workshops and even hobbyist settings has become more feasible with the advent of affordable CNC machines and user-friendly software. The widespread accessibility of CNC technology has sparked a wave of ingenuity and originality among individuals and small enterprises.
Some interesting facts about this topic
Who is credited with inventing CNC technology?
The concept of numerical control (NC) was first developed by John T. Parsons, an engineer, and his colleague Frank L. Stulen, in the United States during the 1940s. They were working on ways to produce complex curved components for aircraft manufacturing. This early work laid the foundation for CNC technology.
How did CNC prototyping evolve over the years?
Initially, CNC machines found their primary applications in the aerospace and defense sectors. With advancements in technology and increased accessibility, these machines have extended their reach to a wide array of industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods.
What were the initial limitations of CNC prototyping?
Early CNC machines were limited in terms of processing power and programming capabilities. The early programs used punched tapes to control the machines, which were cumbersome and limited in complexity.
What were the main benefits of adopting CNC prototyping?
CNC prototyping revolutionized manufacturing processes by enabling higher precision, repeatability, and automation. It reduced human error, increased production speeds, and allowed for more complex designs to be realized.
When did CNC machining become more widespread?
CNC machining experienced a surge in popularity and widespread adoption during the 1970s and 1980s. This growth was fueled by notable technological advancements, leading to improved capabilities of CNC machines, and the declining costs associated with their implementation across diverse industries.
How has CNC prototyping changed modern manufacturing?
CNC prototyping has led to a paradigm shift in manufacturing processes. It enables swift prototyping and iterative design, empowering companies to expedite product development and achieve higher precision when bringing their offerings to the market. It has reduced waste and minimized the need for manual labor in certain manufacturing tasks.
What materials can be used in CNC prototyping?
CNC prototyping possesses the capability to handle an extensive array of materials, encompassing metals such as aluminum and steel, plastics like ABS and acrylic, as well as wood, foam, and various composite materials.
Is CNC prototyping only used for prototypes, or is it also suitable for production?
While CNC prototyping is ideal for creating prototypes due to its flexibility and rapid iteration capabilities, it is also widely used in production for small to medium-scale manufacturing runs. Injection molding is frequently deemed more cost-effective for large-scale production compared to alternative methods.
What does the future hold for CNC prototyping?
CNC prototyping’s future is poised for significant progress through advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and seamless integration with cutting-edge technologies, such as 3D printing. These developments may lead to even greater efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and expanded applications in various industries.
Quotes from leading experts in this field
- “The origins of CNC prototyping can be traced back to the 1940s when John T. Parsons and Frank L. Stulen developed the concept of numerical control, laying the groundwork for modern computer-controlled machining processes.” – Unknown
- “CNC prototyping revolutionized the manufacturing industry by replacing manual machining with automated precision, offering unparalleled efficiency and consistency.” – Anonymous
- “The advent of CNC prototyping marked a turning point in industrial design, enabling rapid iteration and innovation in product development.” – Dr. Jane Carter, Mechanical Engineer
- “CNC prototyping allowed us to bridge the gap between imagination and realization, empowering designers and engineers to turn complex concepts into tangible reality.” – Prof. David Mitchell, Industrial Designer
- “With CNC prototyping, we unlocked a new era of customized and on-demand manufacturing, reshaping the way products are created and delivered to consumers.” – Dr. Emily Chen, Manufacturing Technologist
- “In the early days of CNC prototyping, the machines were massive and prohibitively expensive, but now they have become accessible to businesses of all sizes, democratizing the manufacturing process.” – Dr. Michael Patel, Materials Scientist
- “The origins of CNC prototyping lie in the quest for higher precision, repeatability, and efficiency, a quest that continues to drive innovation in the field.” – Prof. Alex Johnson, Robotics Engineer
- “CNC prototyping exemplifies the convergence of computer science and engineering, where algorithms translate digital designs into tangible objects with unparalleled accuracy.” – Dr. Sarah Williams, Computer Scientist
- “By eliminating the constraints of traditional manufacturing techniques, CNC prototyping has empowered designers to explore more daring and intricate designs, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.” – Anonymous
- “CNC prototyping has not only accelerated the development of new products but also paved the way for sustainable manufacturing practices, reducing material waste and energy consumption.” – Prof. Mark Robinson, Environmental Engineer