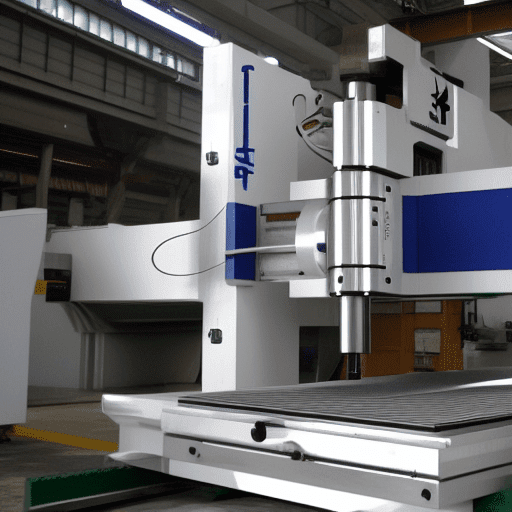
Machining is a manufacturing process that involves the use of specialized tools and machines to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Examples of machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, sawing, and broaching.
Turning is a machining process that involves the use of a lathe to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a chuck and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material. Common materials that are machined using turning include metals, plastics, and wood.
Milling is a machining process that involves the use of a milling machine to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a vise and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material. Common materials that are machined using milling include metals, plastics, and wood.
Drilling is a machining process that involves the use of a drill to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a drill press and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material. Common materials that are machined using drilling include metals, plastics, and wood.
Grinding is a machining process that involves the use of a grinding wheel to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a grinding machine and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material. Common materials that are machined using grinding include metals, plastics, and wood.
Sawing is a machining process that involves the use of a saw to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a saw table and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material. Common materials that are machined using sawing include metals, plastics, and wood.
Broaching is a machining process that involves the use of a broach to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. The material is held in place by a broaching machine and rotated against a cutting tool, which is used to shape the material.
What are the two types of machining?
Machining is a manufacturing process in which parts are cut from a workpiece using a variety of tools. It is a subtractive process, meaning that material is removed from the workpiece to create the desired shape. The two main types of machining are turning and milling.
Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, is used to remove material from a rotating workpiece. The cutting tool is usually held in a tool holder and rotated at a certain speed while the workpiece is fed into the cutting tool. The cutting tool can be a single-point cutting tool, such as a lathe tool, or a multi-point cutting tool, such as a milling cutter. Turning is used to create cylindrical parts with smooth surfaces.
Milling is a machining process in which a rotating multi-point cutting tool is used to remove material from a workpiece. The cutting tool is held in a spindle and rotated at a certain speed while the workpiece is fed into the cutting tool.
What three characteristics are common to machine tools?
Machine tools are specialized pieces of equipment used to shape and form metal and other materials into desired shapes and sizes. They are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. There are many different types of machine tools, but they all share three common characteristics: precision, accuracy, and repeatability.
Precision is the ability of a machine tool to produce parts with exact dimensions and tolerances. This is achieved through the use of high-precision cutting tools and precise machining processes. Accuracy is the ability of a machine tool to produce parts that are within the specified tolerances. This is achieved through the use of high-precision measuring tools and precise machining processes. Repeatability is the ability of a machine tool to produce parts that are identical to each other. This is achieved through the use of high-precision cutting tools and precise machining processes.
These three characteristics are essential for machine tools to produce parts with the desired quality and accuracy.
What are machining processes?
Machining processes are a type of manufacturing process that involve the use of specialized tools and machines to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Machining processes are used to create parts for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products. The most common machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and sawing.
Turning is a machining process that involves rotating a workpiece on a lathe while a cutting tool is used to remove material from the workpiece. This process is used to create cylindrical parts with a uniform diameter and shape.
Milling is a machining process that involves using a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. This process is used to create flat surfaces, slots, and grooves in a workpiece.
Drilling is a machining process that involves using a rotating drill bit to create holes in a workpiece. This process is used to create holes for fasteners, such as screws and bolts.
What is a secondary machining process?
Secondary machining is a type of machining process that is used to refine or improve the surface finish of a part or component that has already been machined. It is typically used to improve the accuracy and precision of the part or component, as well as to improve its aesthetic appearance. Secondary machining processes can include grinding, honing, lapping, polishing, and deburring. Grinding is a process that uses an abrasive wheel to remove material from the surface of a part or component. Honing is a process that uses a honing stone to refine the surface finish of a part or component. Lapping is a process that uses a lapping compound to refine the surface finish of a part or component. Polishing is a process that uses a polishing compound to refine the surface finish of a part or component. Deburring is a process that uses a deburring tool to remove burrs or sharp edges from the surface of a part or component. Secondary machining processes are often used in combination with one another to achieve the desired surface finish.
Is sawing a machining process?
Yes, sawing is a machining process. Machining is a process that involves the use of tools to shape and cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Sawing is a type of machining process that uses a saw blade to cut materials into desired shapes and sizes. Sawing is a common machining process used in many industries, such as woodworking, metalworking, and plastics manufacturing. The saw blade is typically powered by an electric motor, and the material is fed into the saw blade to be cut. The saw blade can be adjusted to cut different shapes and sizes, depending on the material being cut. Sawing is a relatively simple and cost-effective machining process, and it is often used to create parts with complex shapes and sizes.
What is machining in mechanical engineering?
Machining in mechanical engineering is a process of removing material from a workpiece using a cutting tool. It is a subtractive manufacturing process, meaning that material is removed from the workpiece to create the desired shape. Machining is used to create parts with precise dimensions and shapes, and is often used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using other manufacturing processes. Machining is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
The most common machining processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and broaching. Turning is a process of rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool is applied to the surface to remove material. Milling is a process of using a rotating cutting tool to remove material from the surface of a workpiece. Drilling is a process of creating a hole in a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool. Grinding is a process of using an abrasive wheel to remove material from the surface of a workpiece.
What is metal machining?
Metal machining is a process of cutting and shaping metal materials into desired shapes and sizes. It is a manufacturing process that involves the use of specialized tools and machines to remove material from a workpiece in order to create a desired shape or size. The process of metal machining can be divided into two main categories: subtractive machining and additive machining.
Subtractive machining is the process of removing material from a workpiece in order to create a desired shape or size. This is done by using tools such as drills, milling machines, lathes, and grinders. These tools are used to cut away material from the workpiece in order to create the desired shape or size.
Additive machining is the process of adding material to a workpiece in order to create a desired shape or size. This is done by using tools such as welding, brazing, soldering, and casting. These tools are used to add material to the workpiece in order to create the desired shape or size.
What is machining and fabrication?
Machining and fabrication are two processes used to create parts and components from raw materials. Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves cutting away material from a workpiece to create a desired shape or form. This is done using a variety of tools such as lathes, milling machines, and drill presses. The material is cut away in small increments until the desired shape is achieved. Fabrication is an additive manufacturing process that involves joining two or more pieces of material together to create a desired shape or form. This is done using a variety of tools such as welding, riveting, and soldering. The pieces are joined together in a specific order and with a specific technique to create the desired shape. Both machining and fabrication are used in a variety of industries to create parts and components for a variety of applications.
What are the different types of machine?
A machine is a device that uses energy to perform a specific task. Machines can be classified into several different types, depending on the type of energy they use and the task they are designed to perform.
The most common type of machine is the mechanical machine, which uses mechanical energy to perform a task. Examples of mechanical machines include cars, bicycles, and elevators. These machines use mechanical energy, such as the energy from an engine or a motor, to move or lift objects.
Another type of machine is the electrical machine, which uses electrical energy to perform a task. Examples of electrical machines include computers, televisions, and washing machines. These machines use electrical energy, such as the energy from a battery or a generator, to power their components.
A third type of machine is the hydraulic machine, which uses hydraulic energy to perform a task. Examples of hydraulic machines include hydraulic presses, hydraulic lifts, and hydraulic excavators. These machines use hydraulic energy, such as the energy from a pump or a motor, to move or lift objects.
How many types of machine are there?
There are many different types of machines, and the exact number depends on how broadly the term is defined. Generally speaking, machines are devices that use energy to perform a task or function. This could include anything from a simple lever to a complex computer system. Some of the most common types of machines include mechanical machines, such as levers, pulleys, and gears; electrical machines, such as motors and generators; and hydraulic machines, such as pumps and valves. Other types of machines include pneumatic machines, which use compressed air to power tools and machines; and robotic machines, which are automated machines that can be programmed to perform specific tasks. Additionally, there are many other types of machines, such as those used in manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation.
What is the most common machining process?
The most common machining process is turning. Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates. The cutting action of the tool removes material from the workpiece, which is typically metal but can also be wood, plastic, ceramic, or composite material. The process can be done on a lathe or a computer numerical control (CNC) machine.
Turning can be used to create a variety of shapes and sizes, including round, square, hexagonal, and octagonal shapes. It can also be used to create threads, grooves, and other features. The process is often used to create parts for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
The process is relatively simple and can be done with a variety of tools, including single-point cutting tools, multi-point cutting tools, and form tools.
What are the 4 types of manufacturing processes?
The four types of manufacturing processes are:
1. Casting: Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods.
2. Machining: Machining is a manufacturing process in which material is removed from a workpiece using power-driven machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and drill presses. The process can be used to shape or cut a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, and wood.
3. Forming: Forming is a manufacturing process in which a material is shaped by applying pressure to it. This pressure can be applied in a variety of ways, including pressing, rolling, and stretching.