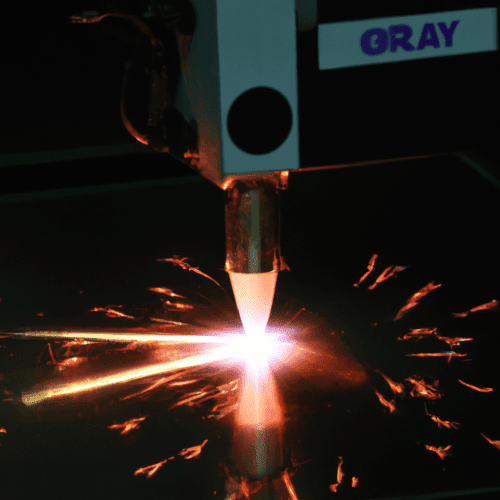
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The gas used in plasma cutting is typically shop air, which is a mixture of mostly nitrogen and oxygen. However, other gases such as argon, hydrogen, and oxygen can also be used depending on the application. The type of gas used will affect the cutting speed, quality, and cost of the process. Shop air is the most common gas used for plasma cutting because it is readily available and relatively inexpensive. Argon is often used for cutting thicker materials because it produces a higher quality cut and is more efficient than shop air. Hydrogen is used for cutting thin materials because it produces a very hot, fast-moving plasma stream that can cut through thin materials quickly and cleanly. Oxygen is used for cutting stainless steel and other materials that require a very high cutting temperature.
Can you use CO2 for plasma cutting?
Yes, you can use CO2 for plasma cutting. Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The gas used in plasma cutting is typically a combination of oxygen and an inert gas such as argon, nitrogen, or carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is the most commonly used gas for plasma cutting because it is relatively inexpensive and produces a good cut quality. When CO2 is used for plasma cutting, the gas is heated to a very high temperature and then forced through a small nozzle. This creates a high-velocity stream of ionized gas, which is then directed at the material to be cut. The heat generated by the plasma arc melts the material, and the high-velocity stream of gas blows the molten material away, leaving a clean cut. Plasma cutting is a fast and efficient way to cut metal, and it can be used to cut a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
What gas is used in plasma?
Plasma is a state of matter in which a gas is heated to such a high temperature that the electrons become separated from the nuclei of the atoms, resulting in a highly electrically conductive gas. The most common gas used in plasma is a mixture of gases, usually consisting of hydrogen, helium, and sometimes nitrogen or other gases. The exact composition of the gas mixture depends on the application, but hydrogen is the most common component. When the gas is heated to a high enough temperature, the electrons become separated from the nuclei, forming a plasma. This plasma can then be used for a variety of applications, such as welding, cutting, and plasma displays.
Is oxygen used in plasma cutting?
Yes, oxygen is used in plasma cutting. Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The process works by creating an electrical arc between an electrode and the material being cut. This arc is then used to heat the material to its melting point, and the high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) is used to blow the molten material away, leaving a clean cut. Oxygen is used as the plasma gas in most plasma cutting applications, as it is the most efficient and cost-effective gas for the job. Oxygen is also used in combination with other gases such as nitrogen, argon, and hydrogen to create a more efficient cutting process.
Can argon be used in plasma cutting?
Yes, argon can be used in plasma cutting. Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The plasma is created by passing a gas, such as argon, through an electric arc. The arc ionizes the gas, creating a plasma stream that is hot enough to melt the material being cut. The plasma stream is then directed through a nozzle, which focuses the stream and increases its velocity. This high-velocity stream of plasma is then used to cut through the material.
Argon is a popular choice for plasma cutting because it is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with other elements. This makes it ideal for cutting materials that are sensitive to oxidation, such as aluminum. Argon is also relatively inexpensive and easy to obtain, making it a popular choice for plasma cutting.
Which is heavier argon or nitrogen?
The answer to the question of which is heavier, argon or nitrogen, is argon. Argon is a noble gas and is the third most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, making up about 0.934% of the atmosphere. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and non-flammable gas. Argon is heavier than nitrogen because it has a higher atomic weight. The atomic weight of argon is 39.948 g/mol, while the atomic weight of nitrogen is 14.007 g/mol. This means that argon is about 2.86 times heavier than nitrogen. Argon is also denser than nitrogen, with a density of 1.784 g/L at 0°C and 1 atm, compared to nitrogen’s density of 1.2506 g/L at 0°C and 1 atm. This means that a given volume of argon will weigh more than the same volume of nitrogen.
Can you use compressor air for plasma cutter?
Using compressor air for a plasma cutter is not recommended. Compressor air is not clean enough for a plasma cutter, as it contains moisture and other contaminants that can damage the plasma cutter and reduce its performance. Additionally, the pressure of the air from a compressor is not high enough to provide the necessary power for a plasma cutter.
Plasma cutters require clean, dry air that is free of contaminants, and the air pressure must be between 80 and 120 psi. Compressor air does not meet these requirements, and using it can cause the plasma cutter to overheat, resulting in damage to the machine and a decrease in its performance.
In order to use a plasma cutter safely and effectively, it is important to use the correct type of air. The best option is to use a dedicated air supply, such as a nitrogen tank, which is designed specifically for plasma cutters. This type of air is clean, dry, and has the correct pressure for a plasma cutter.
Do all plasma cutters need air compressor?
No, not all plasma cutters require an air compressor. Some plasma cutters are designed to use a bottled gas, such as propane or acetylene, as the cutting gas. These types of plasma cutters are often referred to as “inert gas” or “gas-only” plasma cutters. Inert gas plasma cutters are typically used for cutting thicker materials, such as steel, and are often used in industrial applications. Inert gas plasma cutters are usually more expensive than air plasma cutters, but they are more portable and require less maintenance.
Air plasma cutters, on the other hand, require an air compressor to provide the cutting gas. Air plasma cutters are typically used for cutting thinner materials, such as aluminum and stainless steel, and are often used in automotive and home repair applications. Air plasma cutters are usually less expensive than inert gas plasma cutters, but they require more maintenance and are not as portable.
Does a plasma cutter use compressed air?
A plasma cutter is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using an electrical arc to heat and melt the material, which is then blown away by a high-velocity stream of compressed air. The compressed air is used to create a plasma arc, which is a high-temperature, electrically charged gas. This arc is then used to cut through the material. The compressed air also helps to cool the plasma arc and the material being cut, which helps to prevent the material from melting too quickly and damaging the cutting tool. The compressed air also helps to reduce the amount of smoke and fumes created during the cutting process.
What is needed for plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting is a process used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It is a fast and cost-effective way to cut metal, and is often used in industrial settings. In order to use plasma cutting, you will need a few key components.
First, you will need a power source. This can be either a high-frequency generator or a plasma cutting power supply. The power source will provide the electrical current needed to create the plasma arc.
Second, you will need a plasma torch. This is the device that will actually cut the metal. It consists of a nozzle, electrode, and a gas supply. The nozzle directs the plasma arc, the electrode creates the arc, and the gas supply provides the plasma gas.
Third, you will need a cutting table. This is the surface on which the metal will be cut. It should be made of a material that is resistant to heat and sparks, such as steel or aluminum.