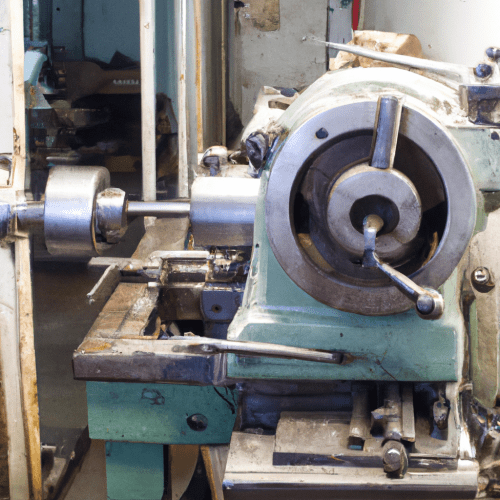
A conventional lathe is a machine tool used for rotating a workpiece on its axis in order to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about an axis of rotation. It is one of the oldest and most widely used machine tools in the manufacturing industry.
A conventional lathe consists of a bed, headstock, tailstock, and carriage. The bed is a heavy, rigid frame that supports the other components. The headstock is mounted on the left end of the bed and contains the motor, gears, and spindle. The tailstock is mounted on the right end of the bed and is used to support the workpiece. The carriage is mounted on the bed and is used to move the cutting tool across the workpiece.
The spindle is the main component of the lathe and is used to rotate the workpiece. It is driven by the motor and is connected to the headstock. The spindle is connected to the headstock by a series of gears, which allow the spindle to rotate at different speeds.
The cutting tool is mounted on the carriage and is used to shape the workpiece. The cutting tool is moved across the workpiece by the carriage, which is driven by a lead screw. The lead screw is connected to the headstock and is driven by the motor.
The workpiece is held in place by the tailstock, which is connected to the bed. The tailstock can be adjusted to accommodate different sizes of workpieces.
Conventional lathes are used to create a variety of objects, including screws, bolts, shafts, and other components. They are also used to create complex shapes and intricate designs.
What is the difference between CNC lathe and conventional lathe?
The main difference between a CNC lathe and a conventional lathe is the level of automation. A CNC lathe is a computer-controlled machine that is programmed to perform specific tasks, such as cutting, drilling, and turning. The machine is programmed with a series of instructions that tell it how to move and what operations to perform. This allows for greater accuracy and repeatability than a conventional lathe.
A conventional lathe is a manually operated machine that is used to shape metal, wood, and other materials. It is operated by a skilled machinist who uses a variety of tools to shape the material. The machinist must be able to read and interpret blueprints and drawings in order to create the desired shape. The machinist must also be able to adjust the speed and feed rate of the lathe in order to achieve the desired results.
CNC lathes are more expensive than conventional lathes, but they offer greater accuracy and repeatability. They are also more efficient, as they can be programmed to perform multiple operations in a single cycle.
What are the 3 types of lathe?
The three main types of lathes are engine lathes, turret lathes, and special-purpose lathes.
Engine lathes are the most common type of lathe and are used for general-purpose turning. They are also known as bench lathes, and are used for a variety of operations such as facing, turning, drilling, reaming, and threading. Engine lathes are usually manually operated and are used for small to medium-sized parts.
Turret lathes are similar to engine lathes, but they are equipped with a turret that can hold multiple cutting tools. This allows the operator to quickly change tools and perform multiple operations in one setup. Turret lathes are used for high-volume production and are usually automated.
Special-purpose lathes are designed for specific operations and are used for complex parts. These lathes are usually computer-controlled and can perform multiple operations in one setup. Examples of special-purpose lathes include CNC lathes, Swiss-type lathes, and multi-spindle lathes.
What do you mean by conventional machining?
Conventional machining is a manufacturing process that uses traditional machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and drill presses to cut and shape materials. It is a subtractive process, meaning that material is removed from the workpiece to create the desired shape. Conventional machining is used to create parts with precise dimensions and tolerances, and is often used to create complex shapes and features. It is also used to create parts with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability. The process involves the use of cutting tools such as drills, end mills, and reamers to remove material from the workpiece. The cutting tools are usually made of high-speed steel or carbide and are designed to cut specific shapes and sizes. The cutting tools are held in a tool holder and are driven by a motor, usually a spindle. The cutting tools are guided by a machine tool, such as a lathe or milling machine, which is used to position the cutting tool relative to the workpiece. The cutting tool is then used to remove material from the workpiece in a controlled manner.
What is the difference between conventional and non conventional machining process?
Conventional machining processes are those that use traditional tools and methods to shape and form materials. These processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and sawing. These processes are used to create parts with precise dimensions and tolerances. They are also used to create parts with complex shapes and features.
Non-conventional machining processes are those that use non-traditional tools and methods to shape and form materials. These processes include electrical discharge machining (EDM), laser cutting, water jet cutting, and electrochemical machining (ECM). These processes are used to create parts with complex shapes and features that are difficult to achieve with conventional machining processes. They are also used to create parts with very tight tolerances and high surface finish.
The main difference between conventional and non-conventional machining processes is the tools and methods used to shape and form materials. Conventional machining processes use traditional tools and methods, while non-conventional machining processes use non-traditional tools and methods.
How does a CNC lathe machine work?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe machine is a type of automated lathe that is controlled by a computer program. It is used to produce precise parts with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability. The CNC lathe machine works by taking a blank piece of material, such as metal or plastic, and using a cutting tool to shape it into the desired shape. The cutting tool is mounted on a spindle that is driven by a motor. The motor is controlled by a computer program that is programmed with the desired shape and dimensions of the part.
The CNC lathe machine is programmed with a series of instructions that tell the machine how to move the cutting tool and the material in order to create the desired shape. The instructions are written in a computer language called G-code. The G-code is a set of instructions that tell the machine how to move the cutting tool and the material in order to create the desired shape. The instructions are written in a language that the computer can understand and interpret.
Which is not the advantage of CNC machines?
CNC machines are computer-controlled machines that are used to automate the production of parts and components in a variety of industries. They offer a number of advantages over traditional manual machining, including increased accuracy, improved productivity, and reduced labor costs. However, there is one disadvantage of CNC machines that should be noted: they require a significant upfront investment. CNC machines are typically more expensive than manual machines, and require specialized training and software to operate. Additionally, CNC machines are not as versatile as manual machines, as they are limited to producing parts that are designed to be machined with a CNC machine. Therefore, if a manufacturer needs to produce a part that cannot be machined with a CNC machine, they will need to use a manual machine or outsource the job to a third-party.