Milling is a versatile and highly efficient machining method that utilizes a rotating multi-blade tool to process the surface of a workpiece, giving it the desired shape and dimensions. It is a key process in various industries, from automotive to manufacturing.
Understanding the Milling Machine
Milling machines play a pivotal role in the milling process. They consist of key components that facilitate precision machining:
- Spindle: The core component that holds the cutting tool and executes the cutting action.
- Worktable: The platform where the workpiece is securely fixed for machining.
- Feed Controls: Mechanisms regulating the movement of the workpiece and cutting tool for precision operations.
Types of Milling Operations
Milling offers a diverse range of operations tailored for specific machining needs:
- Face Milling: Used to achieve flat surfaces and contours, utilizing a face milling cutter.
- End Milling: Creates slots, contours, and flat surfaces precisely using end mills.
- Peripheral Milling: Shaping profiles and closed geometries on the workpiece with various cutters.
- Slot Milling: Employed to create slots and grooves in the workpiece.
The Milling Process Step by Step
The milling process involves several steps
- Workpiece Preparation: Selecting the workpiece material and dimensions, and securely fixing it to the milling machine’s worktable.
- Tool Selection: Choosing the appropriate milling cutter based on the desired geometry and material, and determining cutting parameters.
- Machine Setup: Mounting the selected cutter onto the milling machine’s spindle and adjusting positions for precise machining.
- Feeding and Cutting: Engaging the milling machine’s feed controls to initiate the cutting action, removing material and shaping the workpiece.
Factors Affecting Machining Accuracy
Several factors influence machining accuracy:
- Rigidity: Overcoming machine tool rigidity is crucial for achieving target accuracy in machining.
- Thermal Deformation: Objects expand with rising temperatures, necessitating temperature management during machining.
- Cutting Resistance: Consideration of resistance produced by different tools and materials to optimize machining.
- Speed: Balancing efficiency and accuracy by controlling the machining speed based on tool life and resistance.
- Temperature: Managing temperature changes during machining, especially in large machining areas, using cutting fluids for cooling.
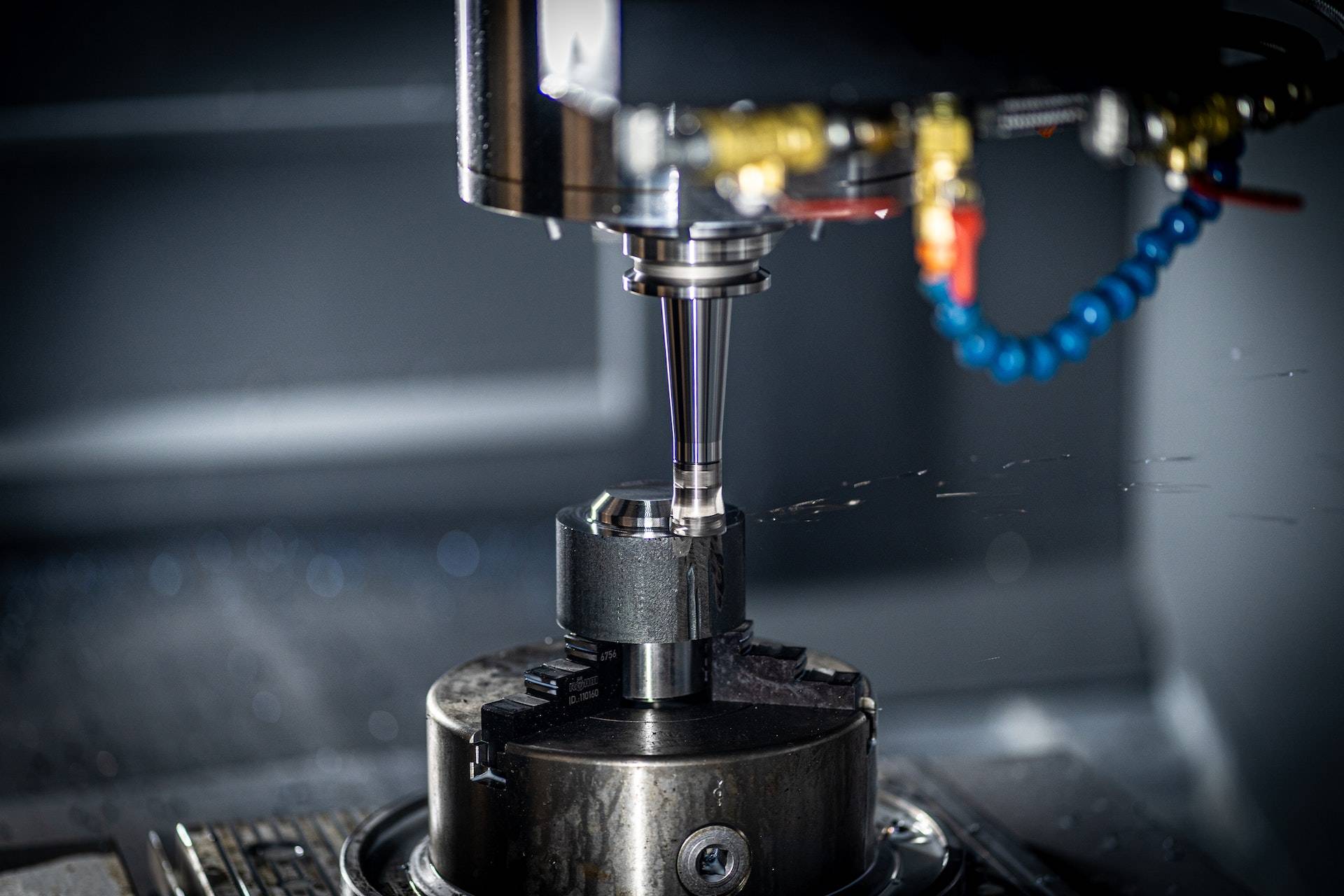

Important Maintenance Tips for Milling Machines
To ensure milling machines remain in optimal condition, these maintenance tips are essential:
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication ensures smooth movement of milling head tools and prolongs their lifespan.
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning after use prevents machine parts from accumulating dust and contaminants, avoiding potential issues.
- Daily Inspection: Performing daily inspections helps detect and prevent problems before they escalate.
What do experts have to say about this?
- John Anderson, CNC Machine Specialist: “Regular and proper maintenance is the key to maximizing the lifespan and performance of milling machines. Paying attention to cleanliness, lubrication, and alignment will significantly reduce downtime and ensure consistent precision in machining operations.”
- Dr. Emily Roberts, Manufacturing Engineer: “Keeping a detailed maintenance schedule is essential for ensuring the longevity of milling machines. Routine inspections and timely replacement of worn-out parts can prevent costly breakdowns and production delays.”
- David Lee, CNC Machinist: “Proper lubrication is critical for the smooth functioning of milling machines. It’s essential to use high-quality lubricants and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid premature wear and tear.”
- Sarah Nguyen, Maintenance Supervisor: “Encourage operators to be vigilant about cleanliness in and around the milling machine. Chips and debris can accumulate and lead to serious damage if not cleaned regularly.”
- Michael Turner, CNC Machine Technician: “Regularly check and adjust the machine’s alignment, including the spindle, worktable, and tool changer. Misalignments can cause inaccuracies in machining and affect the overall performance of the milling machine.”
- Dr. Lisa Thompson, Mechanical Engineer: “Create a comprehensive maintenance checklist that covers all critical components of the milling machine. This will ensure that no essential maintenance tasks are overlooked, maintaining the machine’s reliability.”
- Robert Adams, CNC Service Technician: “Train operators on basic maintenance tasks to empower them to perform routine checks and minor repairs. This proactive approach can catch potential issues early and minimize the need for external repairs.”
- Jessica Martinez, CNC Machine Operator: “Always follow the safety guidelines and lock-out/tag-out procedures when performing maintenance tasks on the milling machine. Safety should be the top priority during any maintenance operation.”
- Frank Davis, CNC Machine Maintenance Manager: “Invest in high-quality replacement parts and components from reputable suppliers. Using genuine parts ensures compatibility and reliability, preventing compatibility issues and enhancing the machine’s performance.”
- Dr. Paul Miller, Manufacturing Consultant: “Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and any issues identified. These records will help track the machine’s maintenance history and plan for future maintenance needs.”