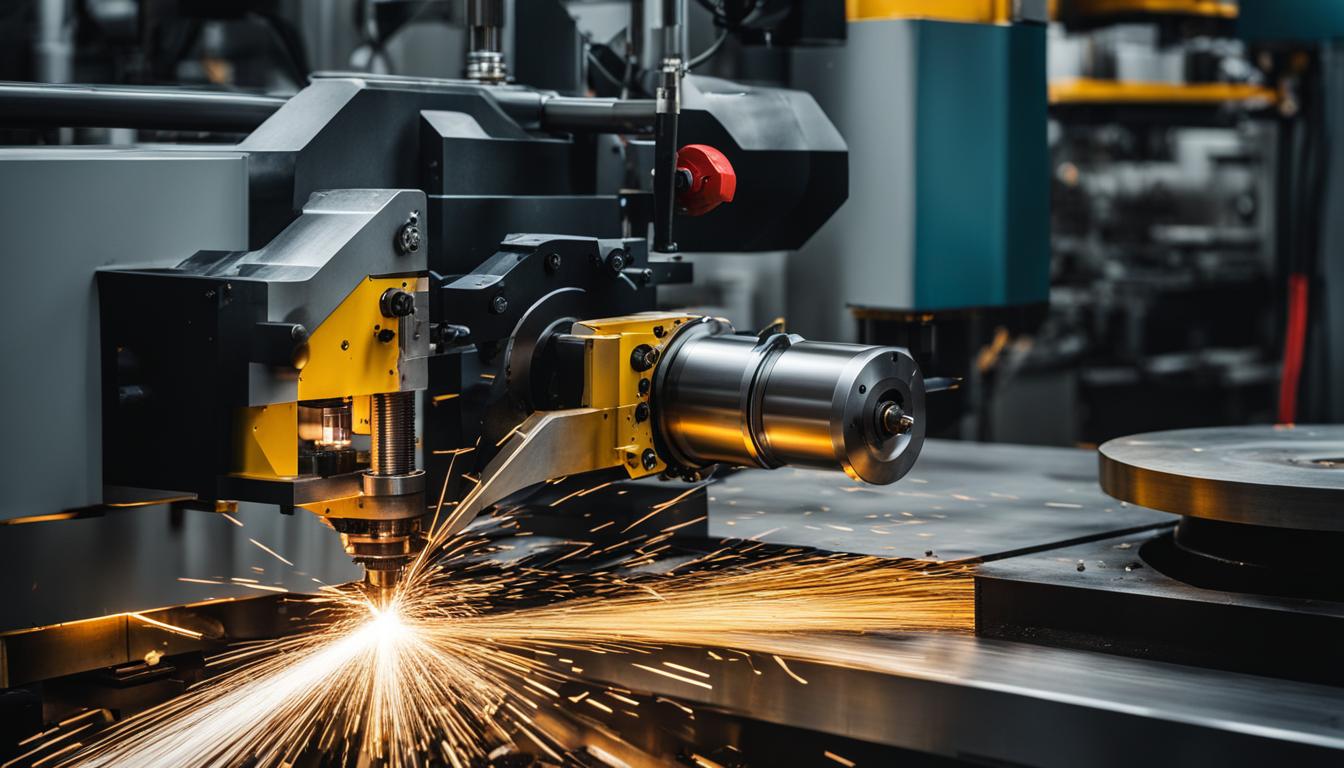
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, a revolutionary technology that has transformed modern manufacturing processes. This automated system uses computer software to control the movement and operation of machine tools, such as lathes, mills, routers, and grinders. CNC machinery operates by following precise, programmed instructions that dictate the tool’s actions, including speed, feed rate, and coordination.
These machines can produce complex three-dimensional shapes with high accuracy and repeatability, making them essential in industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to electronics and medical devices. CNC technology has significantly improved production efficiency, reduced human error, and enabled the creation of intricate parts that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture manually. By integrating computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, CNC machines can translate digital designs directly into physical objects, streamlining the production process and allowing for rapid prototyping and customization.
The versatility and precision of CNC machinery have made it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing, driving innovation and enhancing product quality across various sectors.
- CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, a manufacturing method that automates machine tools through preprogrammed software.
- CNC machines work by following instructions and parameters set in the program, allowing for precise and accurate operations.
- CNC systems offer numerous benefits, including cost reduction, improved worker safety, and greater precision and repeatability.
- CNC machinery finds applications in critical industries such as aerospace, medicine, automotive, electronics, oil and gas, and marine.
- The history of CNC technology dates back to the invention of the first numerical control machine in 1949, marking the beginning of a revolutionary era.
How CNC Machines Work
CNC machines, which stand for Computer Numerical Control machines, are highly advanced tools that operate using preprogrammed software and code. These machines are designed to control the movement and functionality of various cutting tools and machine components, allowing for precise and accurate machining operations.
At the core of CNC technology is the ability to follow instructions and parameters set in the program, such as feed rate and positioning. This enables the machine to perform tasks like milling and cutting with exceptional precision and consistency. The program, containing the necessary instructions, is loaded onto a machine control unit (MCU) before the machining process begins.
Prior to running the actual job, a test run is often performed to ensure that the machine is properly positioned and set up for optimal performance. During this test run, the machine moves according to the code provided and verifies that all actions and functions are executed accurately.
Once the CNC machine is ready, it can perform a wide range of operations, including milling, cutting, drilling, and shaping various materials such as metal, plastic, and wood. The use of advanced technologies, such as high-speed spindles and multi-axis movement, further enhances the flexibility and capabilities of CNC machines.
| CNC Technology Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Precision and Accuracy | Eliminates human errors and ensures consistent results |
| Efficiency and Productivity | Reduces production time and increases output |
| Flexibility and Versatility | Capable of handling various machining operations and materials |
| Automation and Control | Minimizes the need for manual intervention and enhances process control |
| Complex Machining Capabilities | Enables the creation of intricate designs and shapes |
Benefits of CNC Systems
In the manufacturing industry, CNC systems offer numerous advantages that contribute to improved efficiency and productivity. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
1. Cost Reduction
CNC machines are highly cost-effective. By automating the manufacturing process, companies can minimize labor costs and reduce the need for manual intervention. Additionally, CNC machining reduces material waste, resulting in significant savings over time.
2. Improved Worker Safety
With CNC machines, operators have limited direct interaction with hazardous tools and materials. This significantly improves worker safety by minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
3. Greater Precision and Repeatability
Human error is greatly reduced in CNC machining, leading to superior precision and consistent results. CNC equipment can reproduce complex designs and intricate patterns with unmatched accuracy and repeatability.
4. Contour Machining Capabilities
CNC machines are capable of executing intricate contour and complex shape machining tasks. This enables the production of components with intricate designs that would otherwise be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional machining methods.
5. Faster MCU Programming with CAD and CAM Integration
CNC machines leverage Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which simplifies and accelerates the programming process. Integration with CAD and CAM eliminates manual coding and streamlines the programming workflow.
6. Improved Operational Intelligence with ERP Integration
By integrating CNC systems with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, manufacturers gain enhanced operational intelligence. This integration enables real-time data monitoring, production scheduling optimization, and resource management, leading to improved overall efficiency.
7. Reduced Production Bottlenecks
CNC machinery minimizes production bottlenecks through automated operations and continuous processing. With reduced setup times and increased machine uptime, companies can meet production deadlines more efficiently, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
These advantages make CNC systems invaluable assets in the manufacturing industry. By harnessing the power of CNC machinery, companies can achieve higher production output, improved quality control, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Applications of CNC Machinery
CNC machinery has a wide range of applications across critical industries, including aerospace, medicine, automotive, electronics, oil and gas, and marine. Let’s explore how CNC machines are utilized in each sector.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry heavily relies on CNC machining to manufacture components with high precision and accuracy. CNC machines are essential for producing engine parts, structural components, landing gear, and intricate aircraft interior elements.
Medical Sector
In the medical field, CNC machines play a crucial role in producing specialized and high-quality medical equipment and devices. From surgical instruments to prosthetics and dental implants, CNC machining ensures the precise manufacturing of intricate medical components.
Automotive Industry
CNC machining is widely used in the automotive industry for various applications. From prototyping to mass production of parts, CNC machines enable the manufacturing of complex engine components, transmission parts, chassis components, and interior accessories with exceptional precision.
Electronics Industry
The electronics industry heavily relies on CNC machines for the production of consumer electronics, semiconductors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs). With CNC machining, electronic manufacturers can ensure the precise fabrication of intricate circuitry and delicate electronic components.
Oil and Gas Industry
CNC machining plays a crucial role in the oil and gas industry for the manufacturing of drilling rigs and refineries. From precision drilling components to specialized equipment, CNC machines enable the production of reliable and accurate parts used in drilling operations and refineries.
Marine Industry
In the marine industry, CNC machines are used to manufacture precise parts for boats and marine equipment. From propellers to hull components, CNC machining delivers high-quality and accurate parts that ensure the optimal performance and efficiency of marine vessels.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing high-precision components such as engine parts and structural elements. |
| Medical | Precision manufacturing of specialized medical equipment and devices. |
| Automotive | Production of complex engine components, transmission parts, and interior accessories. |
| Electronics | Fabrication of consumer electronics, semiconductors, and printed circuit boards. |
| Oil and Gas | Manufacturing drilling rigs, refineries, and precision drilling components. |
| Marine | Precision manufacturing of boat parts, including propellers and hull components. |
History of CNC Technology
The history of CNC technology can be traced back to the creation of the first numerical control machine by John Parsons in 1949. This groundbreaking invention revolutionized the manufacturing industry by introducing computer automation to control machine tools. Since then, CNC technology has continuously evolved, leading to the development of sophisticated machines that accept CNC programming input and produce precise machine parts with extreme accuracy.
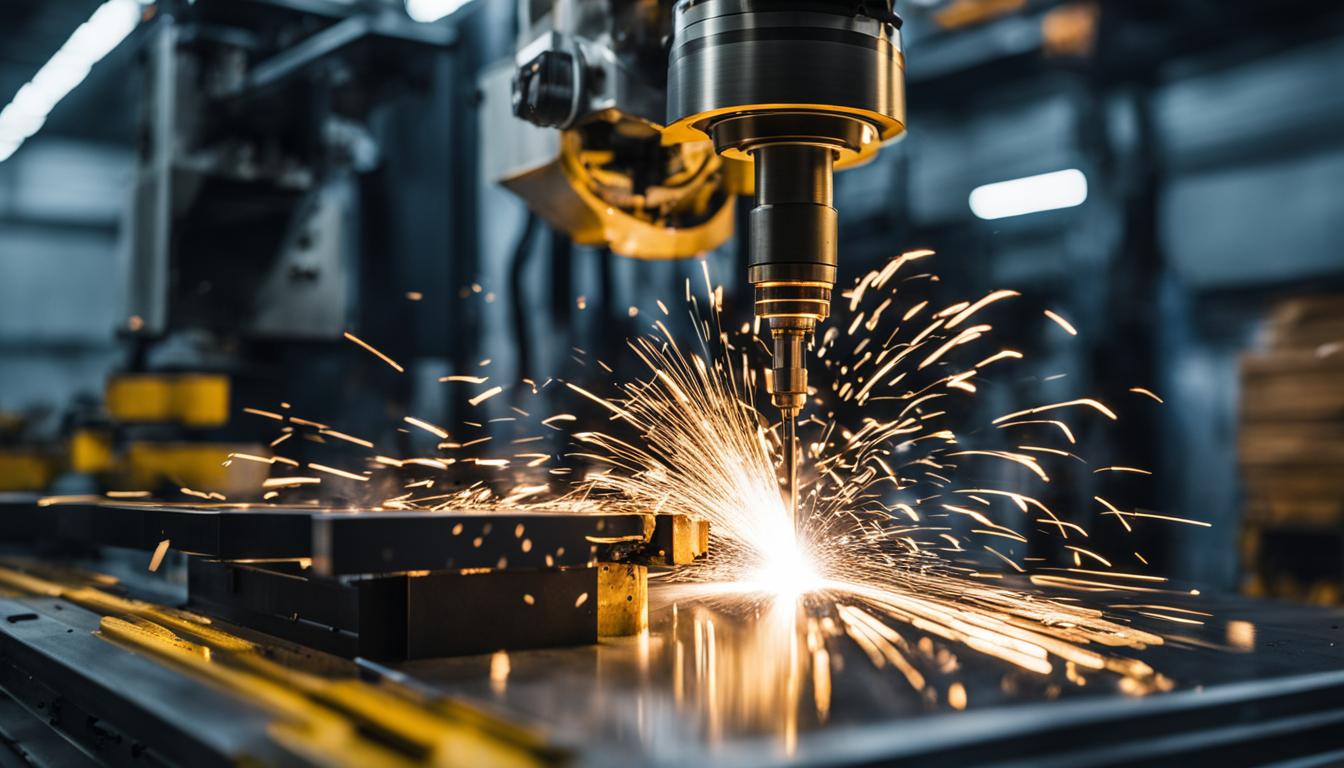

CNC machines have come a long way from their early days of punch tape-controlled devices. Today, they are equipped with advanced software and powerful hardware that enable complex operations and intricate designs. The use of CNC technology has become widespread across various industries, offering numerous advantages such as increased productivity, improved precision, and reduced human error.
Becoming a CNC Machinist
To become a CNC machinist, proper training and education are essential. There are certificate and degree programs available in CNC machining that provide a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes, technical drawings, mathematics, and computer programming skills. Goodwin College, a reputable manufacturing school, offers CNC programs that combine classroom education with hands-on experience using modern CNC technologies. Upon completion of these programs, students can pursue certifications like the National Institute for Metalworking Skills (NIMS) credential to become a CNC operator.
Daily Duties of a CNC Machinist
CNC machinists play a critical role in the manufacturing process, ensuring precision and accuracy in the production of parts and prototypes. They have various daily duties that require technical skill and attention to detail.
One of the primary responsibilities of CNC machinists is reading blueprints and technical drawings. They need to interpret complex diagrams and measurements to understand the specifications of the parts they will be machining.
Once they have a clear understanding of the requirements, CNC machinists set up and operate CNC machines. This involves programming the machine to execute the necessary movements and functions. They input the code for the specific job, which controls the machine’s cutting tools and other components.
Aligning and securing cutting tools and workpieces is crucial for precise machining. CNC machinists carefully position the materials and tools, ensuring that everything is securely in place to avoid errors or accidents during operation.
During the machining process, CNC machinists closely monitor machine feed and speed to ensure optimal performance and prevent any potential issues. They adjust the settings as needed and make sure that the machine is operating at the correct parameters.
Once the machining is complete, CNC machinists are responsible for measuring and examining the finished products for defects. They use specialized measuring tools and inspection equipment to verify the accuracy and quality of the parts produced.
Finally, CNC machinists present the finished workpieces to customers or supervisors. They carefully inspect the parts one final time to ensure they meet the required specifications and then package and deliver them as needed.
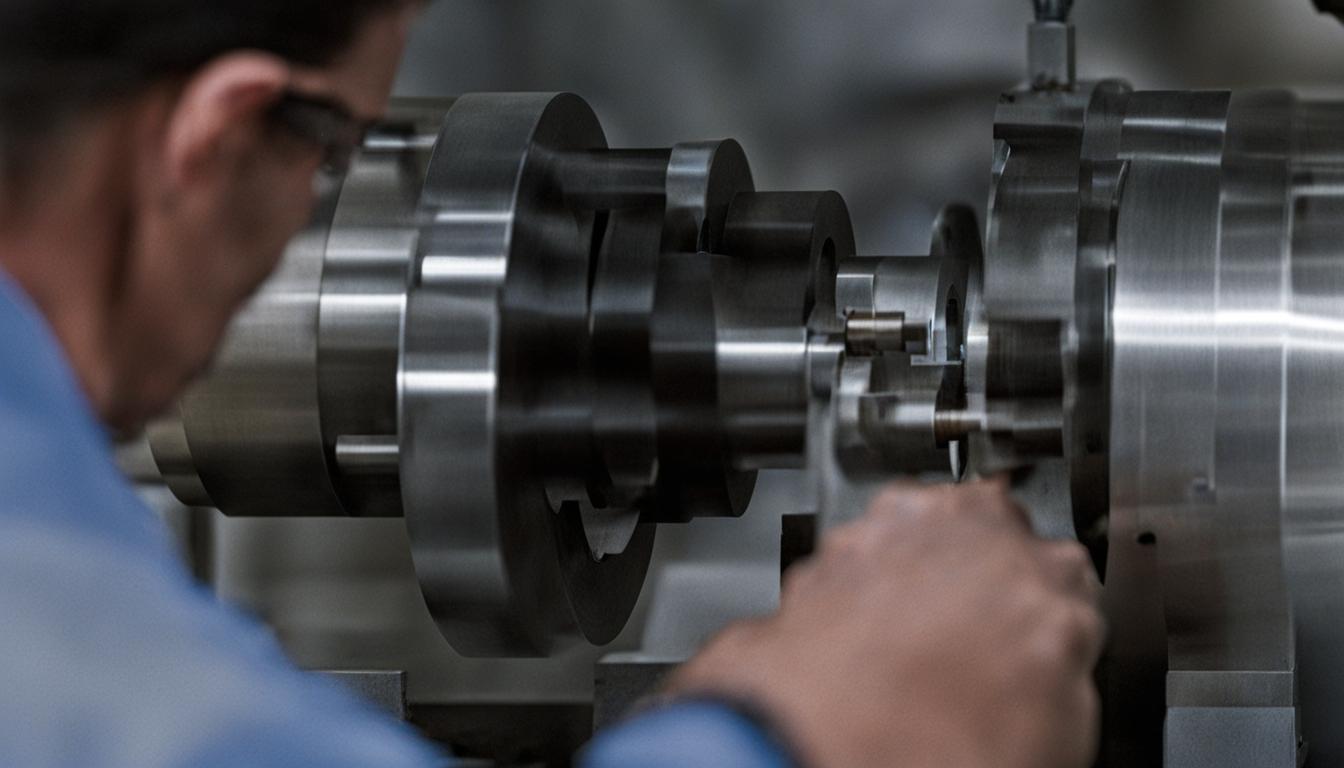
As you can see, the role of a CNC machinist involves a combination of technical knowledge, hands-on skills, and attention to detail. Their work is crucial in maintaining the precision and quality of machined parts in various industries.
The Future of CNC Machining
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, the future of CNC machining looks promising. Advancements in technology are paving the way for more automated and efficient systems, revolutionizing the way products are made. One of the key areas driving this progress is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning with CNC machines.
By combining AI capabilities with CNC technology, manufacturers can improve precision, speed, and efficiency in the machining process. AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time, optimizing tool paths and making adjustments to improve product quality. Machine learning algorithms can also learn from past experiences, continuously improving the machining process and reducing errors.
Another innovative trend in the future of CNC machining is the use of additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, in conjunction with CNC machines. This combination allows for complex designs and shapes that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve. Additive manufacturing techniques can be used to create prototypes, tooling, and even final parts, expanding the design possibilities and reducing production time.
The future of CNC machining holds endless possibilities for innovation and progress. With advanced CNC technology, manufacturers can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and customization in their production processes. By harnessing the power of AI and additive manufacturing, the industry is poised to transform the way we create and manufacture products.
Conclusion
CNC machinery has truly revolutionized the manufacturing industry by bringing about a new era of precision, efficiency, and automation. These advanced machines have become indispensable in various sectors, including aerospace, medicine, automotive, and electronics, among others. Aspiring CNC machinists who undergo proper training and education can look forward to a bright future in this rapidly growing field.
With the right skills and knowledge, CNC machinists play a vital role in the production of high-quality and complex components that meet the stringent demands of modern industries. Their expertise ensures that manufacturing processes are streamlined, errors are minimized, and productivity is maximized.
Looking ahead, the future of CNC machining looks promising. Advancements in technology, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and additive manufacturing techniques, will further propel the capabilities of CNC machinery. The application of AI will enhance precision, speed, and efficiency, while additive manufacturing will offer new design possibilities and greater flexibility.
As CNC machinery continues to evolve and transform the manufacturing landscape, it is crucial for individuals and industries to embrace this technology and stay updated with the latest advancements. By doing so, they can harness the full potential of CNC machinery and unlock endless possibilities in the world of manufacturing.
