CNC robotics combines Computer Numerical Control technology with robotic automation to create highly precise and efficient manufacturing systems. These advanced machines use computer-programmed instructions to control the movement of tools and components, allowing for complex, repetitive tasks to be performed with exceptional accuracy and consistency. CNC robots are capable of handling a wide range of operations, including milling, drilling, cutting, welding, and assembly, across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
By integrating CNC capabilities with robotic flexibility, these systems offer increased productivity, reduced human error, improved safety, and the ability to work continuously without fatigue. CNC robotics also enables manufacturers to produce intricate parts and products that would be difficult or impossible to create manually, while maintaining tight tolerances and high quality standards. As Industry 4.0 continues to evolve, CNC robotics plays a crucial role in smart factories, contributing to enhanced production efficiency, customization capabilities, and overall competitiveness in the global manufacturing landscape.
- CNC robotics combines computer numerical control and robotics technology to improve manufacturing processes.
- CNC machines use pre-programmed software to control their movement and operation.
- CNC robotics offer increased efficiency, accuracy, and precision in mass production and high-precision applications.
- Industries such as aerospace, medical, and electronics benefit from the use of CNC robotics.
- CNC robotics enable faster production times, greater precision, and easier product design changes.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a fundamental process in modern manufacturing that utilizes computer-assisted instructions to transform three-dimensional CAD designs into precise machined parts. By employing code and advanced control technologies, CNC machines deliver exceptional levels of precision, accuracy, and tolerance. In fact, CNC machines can achieve tolerances as fine as 4 μm, surpassing the capabilities of manual machines. The benefits of CNC machining are vast and include enhanced manufacturing precision, smooth surface finish, high dimensional accuracy, and compatibility with a wide range of materials.
Advantages of CNC Robotics for Manufacturing Parts
CNC robotics offer numerous benefits for manufacturing parts. These advanced systems combine the precision and accuracy of CNC machines with the versatility and efficiency of robotics, resulting in improved productivity and quality. Here are some key advantages of using CNC robotics in the manufacturing industry:
1. High Speed and Efficiency
CNC robotics enable high-speed production, allowing manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and increase overall efficiency. These systems can perform repetitive tasks quickly and consistently, minimizing production time and maximizing output.
2. Increased Manufacturing Precision
With CNC robotics, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of precision and accuracy in the production of machine parts. These systems follow pre-programmed instructions with utmost precision, resulting in minimal errors and consistent quality.
3. Smooth Surface Finish
CNC robotics ensure a smooth surface finish of manufactured parts, eliminating the need for additional post-processing operations. This not only saves time but also improves the overall aesthetics of the final product.
4. High Dimensional Accuracy
By combining the computational precision of CNC machines with the dexterity of robotics, CNC robotics can achieve exceptional dimensional accuracy in the manufacturing process. This is especially crucial for industries that require precise measurements and tight tolerances.
5. Compatibility with Different Materials
CNC robotics can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and more. This versatility allows manufacturers to cater to various industries and produce parts for different applications.
6. Faster Production Times and Reduced Labor Costs
By automating the manufacturing process, CNC robotics significantly reduce production times and labor costs. These systems can operate continuously, without breaks or fatigue, resulting in increased productivity and cost savings.
7. Improved Quality and Consistency
CNC robotics deliver consistent results and superior quality, as they eliminate the potential for human error and variability. Manufacturers can rely on these systems to maintain the same level of quality throughout the production process.
8. Increased Flexibility
CNC robotics offer enhanced flexibility in manufacturing, allowing for easy adaptability to changing product designs and specifications. This flexibility enables manufacturers to quickly respond to market demands and incorporate design changes without significant downtime.
9. Automation of Material Handling and Part Loading
With CNC robotics, the handling of materials and loading of parts can be automated, further streamlining the manufacturing process. This automation reduces the need for manual intervention, increases efficiency, and minimizes the risk of injuries.
In summary, CNC robotics technology provides a wide range of benefits for manufacturing parts. From improved speed and precision to increased flexibility and automation, these advanced systems optimize production processes and drive overall efficiency. With their diverse applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics, CNC robotics continue to revolutionize the manufacturing industry.
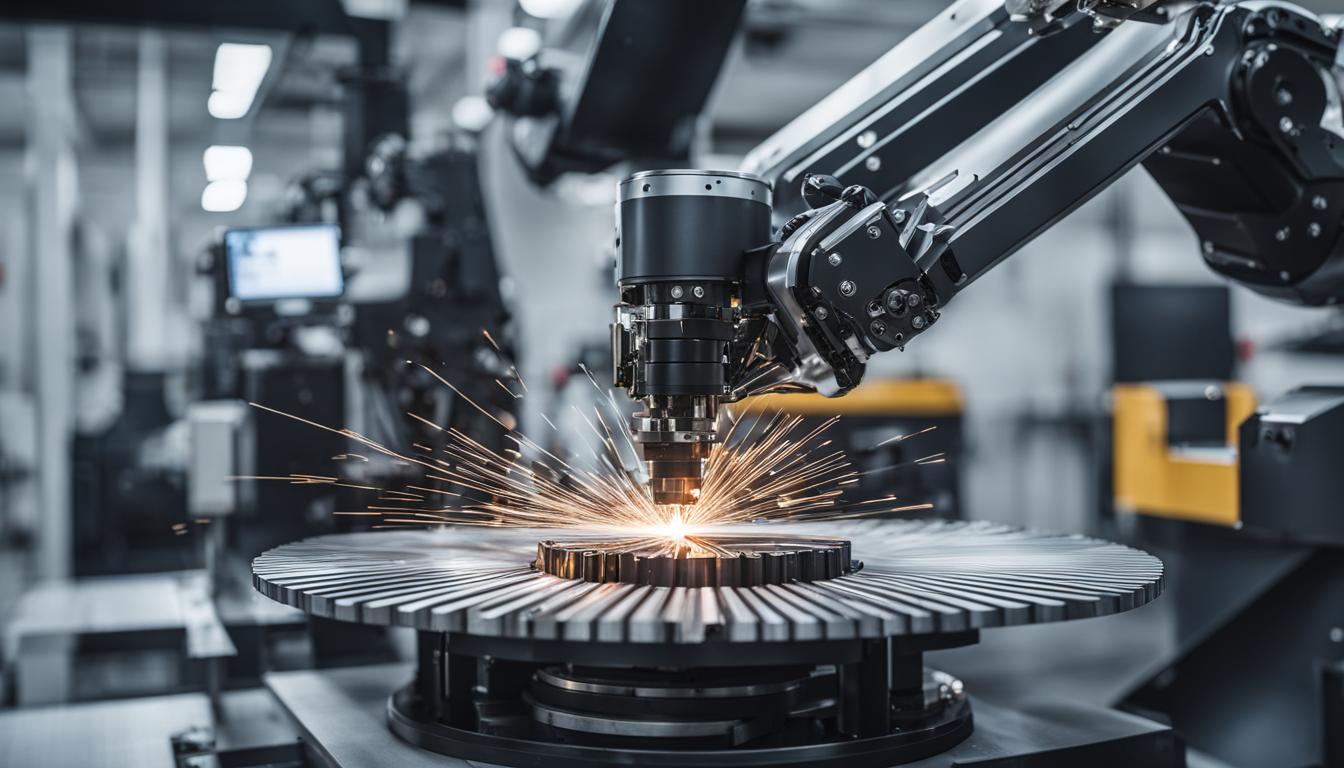

Robot Components Made with CNC Machining
CNC machining plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of various components for robots. From robot arms to jigs and fixtures, CNC technology proves essential in creating these vital elements that drive automation in industries such as industrial automation, automotive, and material handling.
- Robot Arms: Mechanical arms that mimic human arm movements are commonly made using CNC machining. These robot arms enable precise and efficient material handling, assembly, and other tasks in diverse industries.
“Robot arms fabricated through CNC machining provide the accuracy and repeatability needed in industries like industrial automation, automotive, and material handling.”
- Jigs and Fixtures: CNC machines are utilized to fabricate jigs and fixtures, which are vital tools in holding workpieces securely during robotic operations. These components ensure precise positioning and alignment, improving the overall automation process.
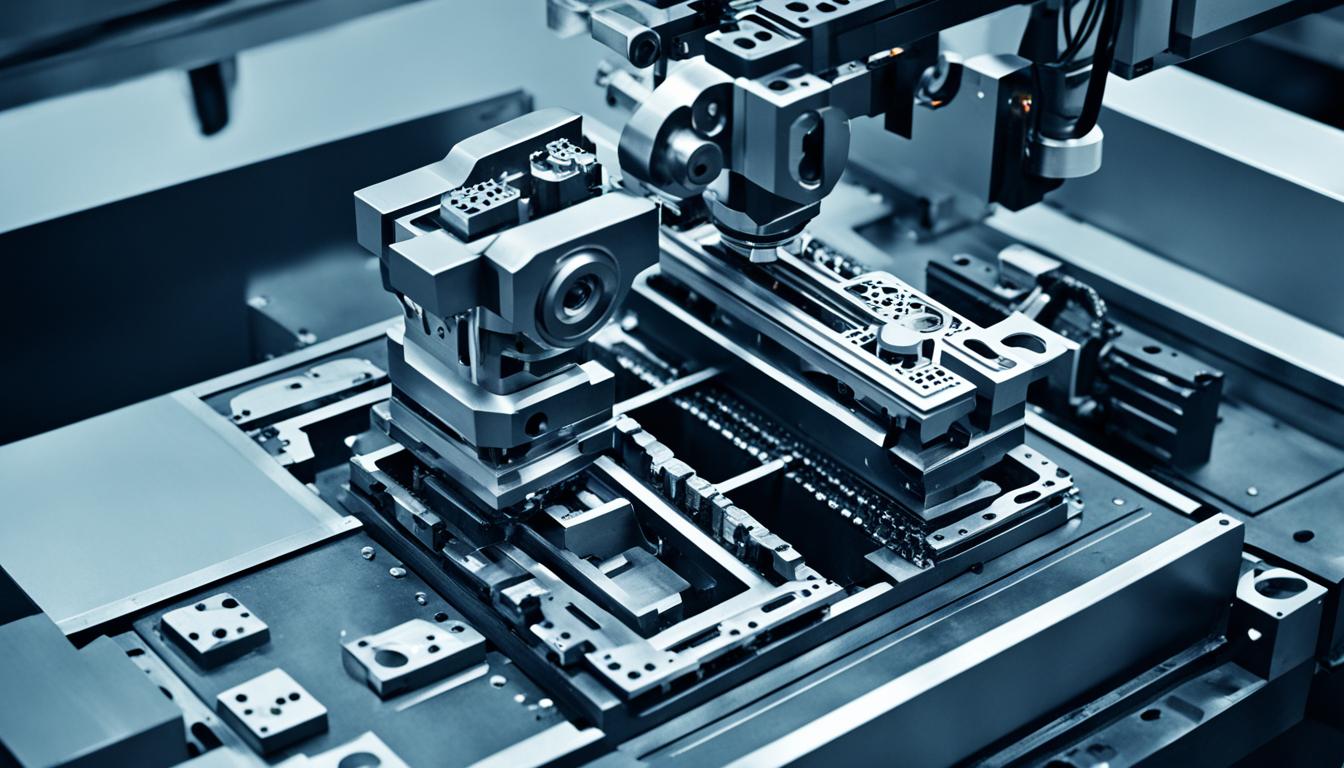
- End Effectors or Grippers: CNC machining is employed in the creation of end effectors or grippers, which are essential tools attached to robot arms. These components enable robots to manipulate and grasp objects with accuracy and precision.
Example: End Effector Image
- Controllers and Sensors: CNC machining also plays a pivotal role in producing controllers and sensors for various robotic machining operations, including printed circuit boards (PCBs). These components ensure seamless communication between the robot and its system.
| Component | Role | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Robot Arms | Mechanical arms that mimic human arm movements | Articulated robot arm |
| Jigs and Fixtures | Tools used for holding workpieces during robotic operations | Fixture for precise alignment |
| End Effectors or Grippers | Tools attached to robot arms for manipulating and grasping objects | Parallel gripper for object manipulation |
| Controllers and Sensors | Components that facilitate communication and control within the robotic system | Printed circuit board (PCB) for robotic control |
Integrating CNC Machines and Automation
Integrating CNC machines with automation, such as robots, has revolutionized manufacturing processes. By combining the precision of CNC machining with the efficiency of automation, businesses can achieve more productive and streamlined operations.
Robots play a crucial role in material handling, part loading and unloading, while CNC machines excel at performing specific machining tasks with exceptional accuracy. Together, this integration offers a myriad of benefits that enhance manufacturing capabilities across various industries.
The Benefits of Integrating CNC Machining and Automation
1. Increased Productivity: Automation eliminates manual tasks, enabling higher production rates and faster cycle times. With robots handling repetitive and labor-intensive jobs, CNC machines can focus on precision machining, resulting in enhanced overall productivity.
2. Reduced Labor Costs: By automating material handling and part loading, businesses can significantly reduce labor expenses. Robots operate continuously, eliminating the need for breaks and shifts, while also minimizing the risk of human error.
3. Improved Quality: CNC machines are renowned for their ability to achieve high dimensional accuracy and surface finish. By integrating automation, these qualities are maintained consistently, ensuring superior product quality and reducing the chances of errors or defects.
4. Increased Flexibility: CNC robotics automation allows for quick and easy changeovers, making it possible to adapt to different product designs or variations. This flexibility enables manufacturers to meet customer demands promptly and efficiently.
5. Reduced Cycle Times: With the efficiency of automation and the precision of CNC machining, cycle times can be significantly reduced. This leads to faster production, shorter lead times, and improved customer satisfaction.
6. Automation of Material Handling and Part Loading: Robots excel at handling heavy or delicate parts, eliminating the risk of damage or injuries. By automating this process, manufacturers can ensure a safer work environment while optimizing efficiency.
“Integrating CNC machines with automation allows manufacturers to harness the benefits of both technologies, resulting in improved productivity, reduced costs, and enhanced product quality.”
However, integrating CNC machines and automation does come with its challenges. The initial costs of implementing automated systems can be considerable, as they require significant investments in both machinery and infrastructure. Additionally, specialized skills and expertise are needed to operate and maintain these systems, necessitating comprehensive training programs for operators and maintenance personnel.
The integration process itself can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and coordination between different technologies and processes. Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach and a long-term commitment to reap the full benefits of integrating CNC machining and automation.
Overall, the integration of CNC machines and automation represents a significant advancement in manufacturing technology. By leveraging the strengths of both systems, businesses can achieve higher productivity, improved quality, and greater efficiency, paving the way for future growth and success.
The Future of CNC Robotics
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CNC robotics holds immense potential for advancing manufacturing processes. With ongoing advancements in CNC machining and robotics, coupled with the integration of AI-powered robots, production efficiency is set to soar. These advancements will revolutionize the manufacturing industry, allowing for faster, more accurate, and cost-effective production.
One notable trend in CNC robotics is the rise of collaborative robots. These robots work in harmony with human operators, enhancing productivity and safety in manufacturing facilities. Additionally, the development of smaller and more affordable CNC equipment makes this technology more accessible to a wider range of manufacturers, fueling further growth and innovation in the industry.
Another exciting development in CNC robotics is the adoption of cloud and analytics technologies. Real-time tracking and analysis of CNC operations enable manufacturers to optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and enhance overall performance. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions, leading to improved efficiency and quality in their manufacturing operations.
The impact of CNC robotics is projected to be significant in key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical. As CNC machines become more advanced and versatile, manufacturers in these industries can expect increased production capabilities, improved product quality, and enhanced automation. Furthermore, the global robotics market is expected to experience steady growth as companies recognize the immense value that CNC robotics brings to their operations.