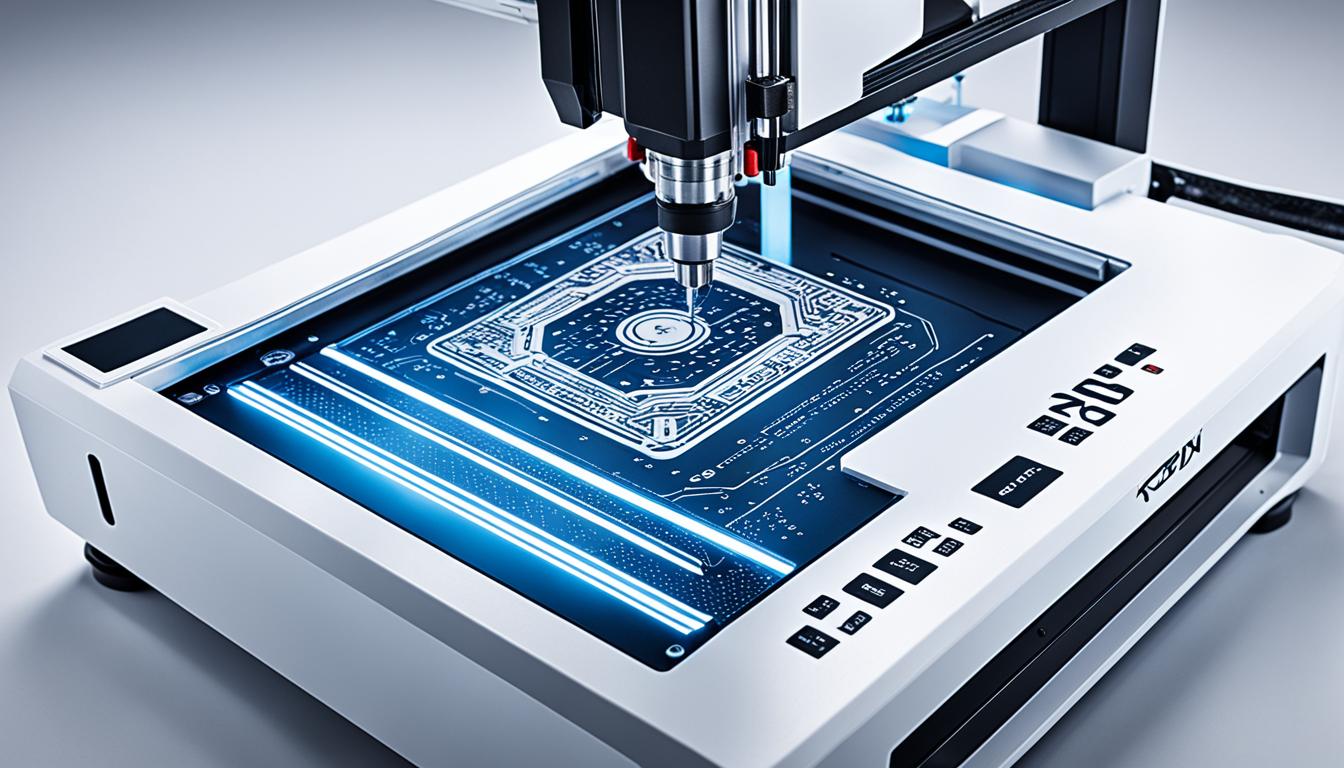
A PCB CNC machine is a specialized computer-controlled device designed for precision manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It uses automated milling and drilling techniques to create intricate circuit patterns on copper-clad boards. These machines employ high-speed spindles and micro-tools to accurately remove copper from the board’s surface, forming conductive tracks and pads according to the PCB design.
PCB CNC machines offer advantages such as rapid prototyping, cost-effectiveness for small-scale production, and the ability to create complex multilayer boards. They typically feature high-resolution stepper motors for precise movement control, vacuum tables to secure the workpiece, and advanced software for translating PCB designs into machine instructions. While primarily used for PCB fabrication, these versatile machines can also handle other materials like aluminum, brass, and plastics, making them valuable tools in electronics manufacturing and prototyping environments.
- PCB CNC machines are specialized mechanical milling machines used in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- These machines utilize a cutting tool called an endmill to remove unwanted copper, creating traces and patterns on the PCB.
- PCB CNC machines offer a faster and more cost-effective method for prototyping and producing custom PCBs compared to traditional etching processes.
- Understanding PCB CNC machines can provide insights into their functions and applications, revolutionizing PCB production in various industries.
The PCB Milling Process
The PCB milling process is a crucial step in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. It involves the use of a specialized machine, known as a PCB router or CNC mill, to cut desired traces and patterns into the copper layers of a PCB blank.
The milling machine utilizes a rotating cutting tool called an endmill to remove material from the copper layer, creating conductive tracks, traces, and holes. The endmill is driven by a spindle motor that spins it at high speeds, typically ranging from 10,000 to 100,000 RPM.
To ensure precise positioning in the X and Y axes, the PCB blank is fixed to a movable bed. This allows for accurate cutting and enables the creation of intricate designs and patterns on the PCB.
The milling depth can be controlled to isolate different copper layers in multilayer PCBs, ensuring the desired functionality and conductivity. The process may involve several steps, including design, setup, copper clearing, drilling, tracing, and finishing.
Overall, the PCB milling process is a versatile and efficient method for producing high-quality circuit boards. It offers greater control and flexibility compared to traditional etching processes, making it an essential technique for various industries.
Advantages of PCB Milling
PCB milling offers several advantages over traditional PCB fabrication methods like etching. These advantages include:
Rapid Prototyping
With PCB milling, you can quickly prototype a single PCB in under an hour. This eliminates the need to submit designs to a fabrication facility and wait for production. It enables designers to iterate and test their PCB layouts more efficiently during the development phase.
Design Flexibility
PCB milling provides unparalleled design flexibility. Changes and new versions can be milled anytime, allowing for faster design iterations. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for projects that require frequent design revisions or customization.
Low Startup Cost
Compared to other PCB fabrication methods, PCB milling has a low startup cost. The cost of a PCB milling machine and accessories is affordable, making it an accessible option for small-scale production. This advantage allows hobbyists, startups, and small businesses to bring their PCB designs to life without breaking the bank.
Complex Board Shapes
Milling enables the creation of complex board shapes that may be difficult or expensive to achieve with other fabrication methods. Whether it’s intricate cutouts or curved contours, PCB milling provides the necessary precision to produce unique board shapes.
Simplified Multilayer Fabrication
Multilayer PCB fabrication can be simplified with the use of PCB milling. Rather than relying on complex and time-consuming processes, milling allows for the isolation of different copper layers in a straightforward manner.
On-Demand Production
With PCB milling, you have the flexibility to produce boards on-demand. This eliminates the need for outsourcing production, reducing lead times and providing greater control over the manufacturing process.
| Advantages of PCB Milling |
|---|
| Rapid Prototyping |
| Design Flexibility |
| Low Startup Cost |
| Complex Board Shapes |
| Simplified Multilayer Fabrication |
| On-Demand Production |
Limitations and Considerations
While PCB milling offers various advantages, it’s important to consider its limitations before utilizing this technology. Understanding these limitations will help ensure that you make informed decisions regarding your PCB production process.
One of the primary considerations is lower trace precision compared to commercial fabrication processes. Typical PCB mills may not achieve tight tolerances, which can affect the overall quality and performance of your circuit board.
Furthermore, PCB milling is better suited for one-off production or small quantities. As the quantity of boards increases, both the time and cost of milling significantly increase, making it less suitable for large-scale production runs. Typical mills also have limitations in terms of board size, maxing out around 12″x12″.
Additionally, there are other factors to consider, such as exposed traces without a solder mask coating. This can affect the durability and longevity of your PCB. You may also need to invest additional design work to create manufacturing files specifically tailored for the milling process.
Lastly, the milling process generates copper waste, which should be properly managed and disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
Although PCB milling has its limitations, it remains a valuable option for one-off production and small-scale projects where customization and rapid prototyping are crucial. By understanding these considerations, you can effectively leverage PCB milling to achieve your desired outcomes.
“It’s crucial to carefully consider the limitations of PCB milling before deciding to utilize this production method. By understanding these limitations upfront, you can effectively manage your expectations and make informed decisions for your PCB manufacturing process.”
How PCB Milling Works
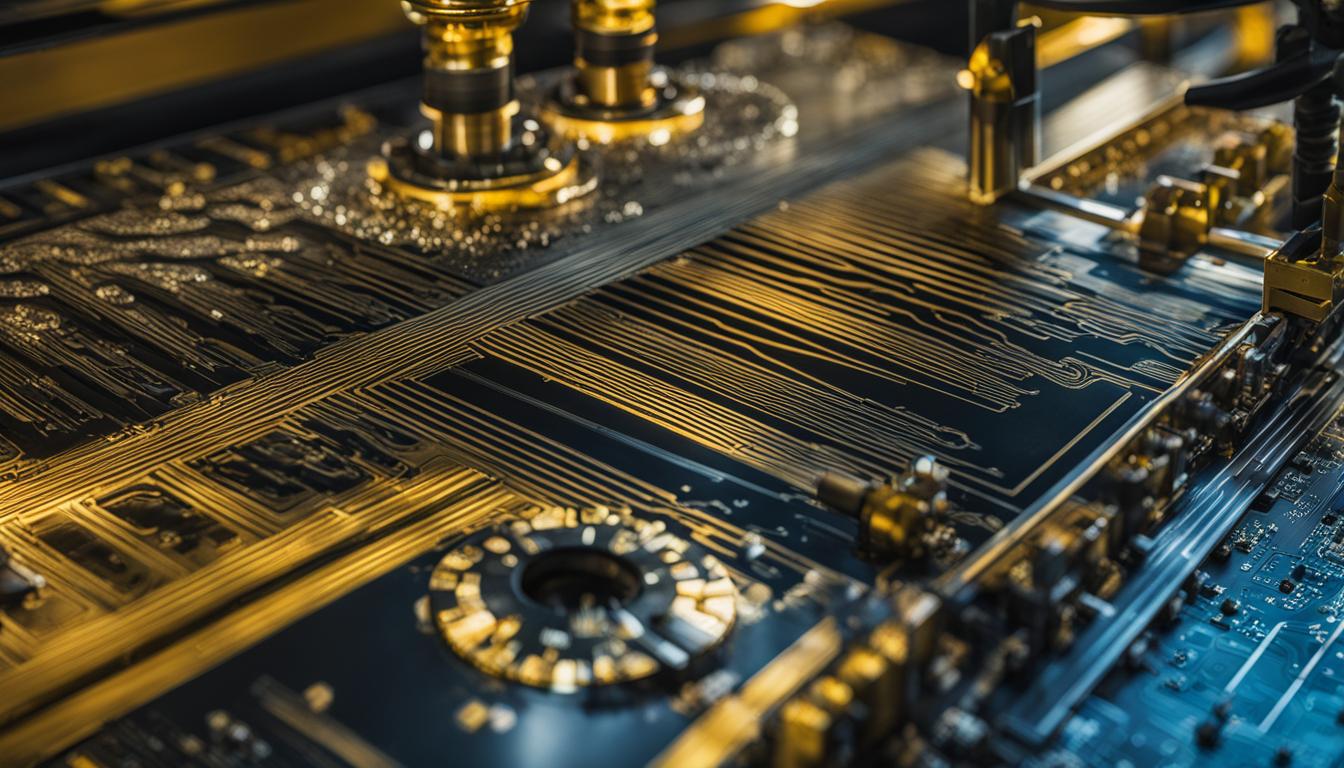
PCB milling is a precise and efficient process that utilizes a milling machine and an endmill to remove material from the copper layers of a PCB blank. The endmill, typically made of hard materials like carbide or diamond, is mounted on a spindle motor, which spins it at high speeds between 10,000-100,000 RPM. The PCB blank is securely fixed to a movable bed, allowing for precise positioning during the milling process.
During PCB milling, the high-speed rotation of the endmill is combined with the movement of the bed in the X and Y axes. This enables complex patterns to be traced into the copper layer, creating the desired PCB features. The process involves steps such as copper clearing, drilling, and tracing to achieve the desired outcome.
The image above depicts a PCB milling machine in action, showcasing the intricate process of material removal using an endmill.
Tools and Software for PCB CNC Milling
To perform PCB CNC milling, you need specific tools and software. The most important tool is the endmill, which comes in different sizes and types for various milling operations. Carbide or diamond endmills are commonly used. Additionally, you will need a PCB holder, such as clamps or vacuum hold-downs, to secure the PCB blank to the milling machine bed.
CAM software is essential for converting PCB designs into toolpaths for the milling machine. Common options for CAM software include Fusion 360, VCarve, and FlatCAM. These tools and software enable precise control over the milling process and help generate the necessary G-code files for the CNC milling machine.
When it comes to tools, having the right endmill is crucial for achieving accurate and high-quality results in PCB CNC milling. Endmills come in different shapes, sizes, and materials, allowing you to choose the most suitable one for your specific milling needs. Carbide endmills are known for their durability and can handle a wide range of materials, while diamond endmills offer exceptional precision and are ideal for milling hard substrates.
Additionally, a reliable PCB holder is essential for securely holding the PCB blank in place during the milling process. Clamps or vacuum hold-down systems are commonly used to ensure stability and prevent any movement or shifting that could affect the milling accuracy.
Moving on to software, CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software plays a crucial role in PCB CNC milling. CAM software takes your PCB design files and generates toolpaths that the milling machine can follow. It enables you to define the cutting parameters, such as the milling depth and speed, and provides a visual representation of the milling process. Fusion 360, VCarve, and FlatCAM are popular CAM software options that offer advanced features and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
Applications of PCB Milling
PCB milling is a versatile process that finds applications in various areas, revolutionizing PCB production for different industries. Let’s explore some of the key applications of PCB milling:
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a significant application of PCB milling. Designers can quickly iterate and test PCB layouts during the development phase, allowing for efficient design optimization. The flexibility offered by PCB milling enables designers to create custom circuits without the setup costs associated with custom fabrication methods.
Custom Circuits
PCB milling provides designers with the capability to create custom circuits tailored to specific requirements. It allows for quick modifications and changes to the circuit design, facilitating rapid customization. This flexibility in creating custom circuits is advantageous for projects that demand unique functionalities or specialized applications.
Repair and Rework
Another important application of PCB milling is in repair and rework processes. When there are minor changes or trace fixes required on existing PCBs, PCB milling offers a precise and efficient solution. It enables the modification of existing boards without the need for complete re-fabrication, saving time and cost.
Education and Academic Labs
PCB milling is commonly used in educational settings and academic labs. It provides students and researchers with the opportunity for hands-on PCB fabrication, enhancing their understanding of the PCB production process. By utilizing PCB milling machines, educational institutions can offer practical training and promote innovation in electronics and engineering disciplines.
Creating Unique Board Shapes
One of the unique advantages of PCB milling is the ability to create intricate board shapes that would be challenging and expensive with other fabrication methods. PCB milling machines can precisely cut complex outlines and shapes, allowing designers to implement innovative and eye-catching designs. This application is particularly relevant for projects that prioritize aesthetics or require unconventional board geometries.
With its wide range of applications, PCB milling offers significant benefits in terms of rapid prototyping, customization, repair and rework, as well as academic and design innovation. Through this technology, designers and manufacturers can streamline their PCB production processes and bring their ideas to life more efficiently and cost-effectively.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Prototyping | Design iteration and testing during development |
| Custom Circuits | Tailored circuits to specific requirements |
| Repair and Rework | Modification of existing boards |
| Education and Academic Labs | Hands-on PCB fabrication and innovation |
| Creating Unique Board Shapes | Intricate and unconventional designs |
Getting Started with PCB Milling
To begin your journey into the world of PCB milling, you’ll need a few essential tools and software. First and foremost, you’ll require a reliable PCB milling machine. There are various options available, ranging from affordable models suitable for hobbyists to professional-grade machines for small-scale production.
Next, you’ll need a selection of endmills in different sizes. These cutting tools are crucial for performing various milling operations and achieving the desired results. Ensure you have a range of endmills that can handle different materials and cutting depths.
In addition, you’ll need a PCB holder to secure the PCB blank during the milling process. This can be in the form of clamps or vacuum hold-downs, depending on the specific requirements of your milling machine.
To generate toolpaths for the milling machine, you’ll need CAM software. Popular options include Fusion 360, VCarve, and FlatCAM. These software programs allow you to convert your PCB designs into precise instructions for the milling machine, ensuring accurate and efficient milling operations.
Once you have all the necessary equipment and software in place, it’s essential to prioritize safety. Invest in proper eye protection to safeguard your vision during the milling process. Additionally, consider using dust and fume extraction systems to maintain a clean and healthy working environment.
When starting out with PCB milling, it’s advisable to begin with simple designs and gradually build your skills and confidence. Practice different milling techniques and familiarize yourself with the capabilities of your machine. As you gain experience, you can move on to more complex milling operations and explore the full potential of PCB milling technology.
By delving into the world of PCB milling, you’ll unlock new possibilities for rapid prototyping and customization. Whether you’re a hobbyist or pursuing small-scale production, PCB milling enables you to bring your PCB designs to life more efficiently and cost-effectively.
