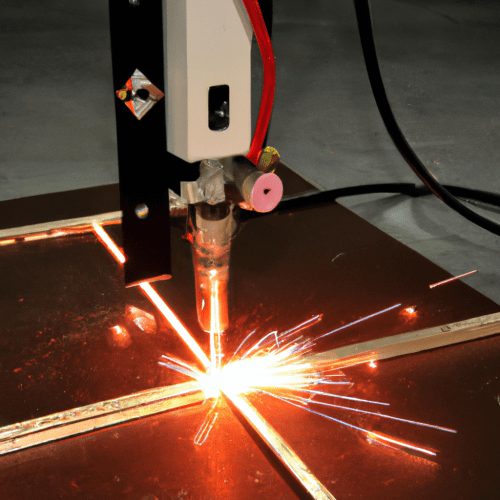
A plasma cutter is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using an electrical arc to heat and melt the material, which is then blown away by a high-velocity stream of gas. In order to use a plasma cutter, you will need the following items:
1. Plasma Cutter: This is the main tool that will be used to cut through the material. It consists of a power supply, a torch, and a nozzle. The power supply provides the electrical current that is used to create the arc, while the torch and nozzle direct the arc and the gas stream.
2. Compressed Air: This is the gas that is used to blow away the molten material. It is usually supplied from an air compressor, and the pressure and flow rate must be adjusted to match the requirements of the plasma cutter.
3. Protective Gear: When using a plasma cutter, it is important to wear protective gear such as safety glasses, gloves, and a welding helmet. This will protect you from the intense light and heat generated by the arc, as well as any sparks or debris that may be created.
4. Work Table: A work table is necessary to provide a stable surface for the material being cut. It should be made of a non-flammable material such as steel or concrete, and should be large enough to accommodate the material being cut.
5. Clamps: Clamps are used to hold the material in place while it is being cut. They should be strong enough to hold the material securely, and should be placed in such a way that they do not interfere with the cutting process.
6. Electrical Outlet: A plasma cutter requires a dedicated electrical outlet in order to operate. The outlet should be rated for the power requirements of the plasma cutter, and should be located close to the work area.
What gas do you need for a plasma cutter?
A plasma cutter is a tool used to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It works by using a high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through the material. The gas used in a plasma cutter is typically a combination of nitrogen and hydrogen, although other gases such as argon, oxygen, and air can also be used. The type of gas used will depend on the type of material being cut and the thickness of the material. For example, nitrogen is often used for cutting thin materials such as sheet metal, while argon is used for thicker materials such as steel. The gas is typically stored in a tank and is connected to the plasma cutter via a hose. The gas is then heated to a high temperature and forced through a nozzle, creating a high-velocity stream of ionized gas that is used to cut through the material.
Do you need a compressor for a plasma cutter?
A compressor is not strictly necessary for a plasma cutter, but it can be beneficial in certain situations. A plasma cutter works by using an electrical arc to cut through metal, and the arc is created by a high-voltage electrical current. The current is generated by a power supply, which is usually powered by a standard wall outlet. However, if you are using a plasma cutter in a remote location or in an area with limited access to power, a compressor can be used to provide the necessary air pressure to power the plasma cutter. Compressors are also useful for providing a consistent air pressure, which can help to ensure a clean and precise cut. Additionally, a compressor can be used to provide a steady stream of air to cool the plasma cutter, which can help to extend its lifespan.
Is it hard to use a plasma cutter?
Using a plasma cutter can be a bit tricky, especially for those who are new to the process. It requires a certain level of skill and knowledge to be able to use a plasma cutter safely and effectively. The most important thing to remember when using a plasma cutter is to always wear the proper safety gear, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a welding helmet. Additionally, it is important to make sure that the plasma cutter is properly set up and that the correct settings are used for the material being cut. It is also important to make sure that the plasma cutter is properly grounded and that the air pressure is set correctly.
When using a plasma cutter, it is important to make sure that the material being cut is properly secured and that the cutting area is free of any debris or obstructions. Additionally, it is important to make sure that the plasma cutter is properly aligned with the material being cut and that the correct cutting speed is used. It is also important to make sure that the plasma cutter is not over-heated and that the cutting area is properly ventilated.
How big of an air compressor do I need to run a plasma cutter?
The size of the air compressor you need to run a plasma cutter depends on the type of plasma cutter you are using. Generally, plasma cutters require a minimum of 4 CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) at 90 PSI (Pounds per Square Inch). However, some plasma cutters require more CFM and PSI than others. For example, a plasma cutter with a higher amperage rating will require more CFM and PSI than a plasma cutter with a lower amperage rating. Additionally, the type of material you are cutting will also affect the size of the air compressor you need. For example, if you are cutting thicker materials, you will need a larger air compressor with more CFM and PSI than if you are cutting thinner materials.
To determine the exact size of the air compressor you need to run your plasma cutter, you should consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the plasma cutter. This will provide you with the exact CFM and PSI requirements for your plasma cutter.
Are plasma cutters worth it?
Plasma cutters are a great tool to have in any workshop, and they can be worth the investment depending on the type of projects you plan to use them for. Plasma cutters are a type of cutting tool that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through metal. They are often used in welding and fabrication projects, and they can be used to cut through a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and stainless steel. Plasma cutters are more efficient than traditional cutting tools, such as oxy-acetylene torches, and they can cut through thicker materials with greater precision. They are also more cost-effective than other cutting tools, as they require less energy and produce less waste.
When deciding if a plasma cutter is worth the investment, it is important to consider the type of projects you plan to use it for. If you are a professional welder or fabricator, a plasma cutter can be a great tool to have in your workshop. It can save you time and money, and it can help you produce higher-quality work.
Can you use CO2 for plasma cutter?
Yes, you can use CO2 for a plasma cutter. Plasma cutters use a combination of electricity and gas to cut through metal. The gas used in a plasma cutter is typically either compressed air or a gas such as oxygen, nitrogen, argon, or carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is a popular choice for plasma cutting because it is relatively inexpensive and readily available. It is also a good choice for cutting thicker metals, as it produces a hotter, more focused arc than compressed air.
When using CO2 for a plasma cutter, it is important to ensure that the gas is clean and dry. Contaminants in the gas can cause the plasma arc to become unstable, resulting in poor cutting performance. Additionally, the gas should be free of moisture, as moisture can cause the arc to become unstable and can also cause the torch to become clogged.
Which plasma gas gives the best results for cutting stainless steel?
When it comes to cutting stainless steel, plasma gas is an important factor in determining the quality of the cut. The best results for cutting stainless steel are achieved when using a combination of argon and hydrogen gas. Argon is an inert gas that is used to shield the cutting area from oxidation, while hydrogen helps to increase the cutting speed and reduce the heat affected zone. The ratio of argon to hydrogen should be adjusted depending on the thickness of the material being cut. For thin materials, a higher ratio of argon to hydrogen is recommended, while thicker materials require a lower ratio. Additionally, the pressure of the gas should be adjusted to ensure the best results. Too much pressure can cause the plasma to overheat, while too little pressure can cause the cut to be too shallow.
When using plasma gas to cut stainless steel, it is important to use the correct gas and pressure settings to ensure the best results. Argon and hydrogen are the best gases for cutting stainless steel, and the ratio of argon to hydrogen should be adjusted depending on the thickness of the material.
What is F5 plasma gas?
F5 plasma gas is a type of gas that is used in a variety of industrial processes. It is a mixture of five gases, including argon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. The gas is created by a process called plasma arc welding, which uses an electric arc to heat and ionize the gas mixture. The resulting plasma gas is then used in a variety of industrial processes, such as welding, cutting, and brazing.
F5 plasma gas is highly efficient and cost-effective, as it can be used to perform a variety of tasks with minimal energy consumption. It is also very safe to use, as it does not produce any hazardous byproducts. Additionally, F5 plasma gas is non-toxic and non-flammable, making it an ideal choice for many industrial applications.
F5 plasma gas is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical. It is also used in the production of semiconductors, as well as in the manufacture of electronic components.